Business grant funding is a highly sought-after resource for entrepreneurs looking to grow without taking on debt. For many startups and expanding companies, securing capital is the most significant hurdle. While loans are a traditional route, they come with the burden of repayment and interest. Grants, on the other hand, offer a powerful alternative, providing the fuel for innovation and expansion without the financial strain. This guide will explain what business grants are, the different types available, how they compare to loans, and how to navigate the application process.
This article explains the key concepts of business grants, helping entrepreneurs understand how they can secure funding to support growth, innovation, and operational development. We specialize in company formation and not in grant application services. For detailed guidance on applying for grants, please consult a qualified expert.
What is a business grant?
A business grant is a sum of money given to a business by a government agency, foundation, or corporation that does not need to be repaid. Unlike a loan, a grant is not a form of debt. Instead, it's considered a form of "non-dilutive financing," meaning you don't have to give up any equity or ownership in your company to receive the funds, nor does it create a repayment obligation.
Grant funding is typically awarded to businesses to achieve a specific objective that aligns with the grantor's mission. These objectives often serve a public good, such as stimulating economic growth, fostering innovation in a particular industry, or supporting businesses owned by underrepresented groups. Therefore, the application process is often rigorous, and the funds usually come with specific stipulations on how they can be used. The granting organization will often require detailed reporting to ensure the money is spent as intended. Grants are typically one-off awards and may not provide consistent funding, so businesses should not rely on them as a long-term financing source. Additionally, the competitive nature of grant applications means not all applicants will be successful.
Types of business grants
Business grants are available from a wide range of sources, each with its own focus and eligibility criteria. Understanding these categories can help you narrow your search and focus on the opportunities that are most relevant to your business.

04 Types of business grants
Government grants
These are often the largest and most competitive grants. They are funded by taxpayer money and are designed to support national or regional economic goals. Governments often utilize these tools to incentivize startup grants and incentives for high-growth potential sectors.
- Federal grants
Federal grants are typically offered by government agencies to stimulate specific sectors like technology, research and development, or environmental conservation. These grants often involve a complex application process and strict regulatory compliance. In the United States, a central resource for finding these opportunities is Grants.gov. - State and local grants
State and local governments also offer grants to encourage business growth within their jurisdictions. These grants may be less competitive than federal ones and are often focused on goals like local job creation or community development. Some state grants are matching grants, meaning the business is required to match the funds they receive.
Corporate grants
Many large corporations have philanthropic arms that offer grants to small businesses. These programs are often part of the company's corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and may be tied to their industry or values. For instance, a tech company might offer grants to startups developing innovative software, while a consumer goods company might support businesses with sustainable practices or green tech initiatives.
Foundation grants
Private foundations and nonprofit organizations are another significant source of grant funding. These grants are often mission-driven, targeting specific social or economic issues. There are foundations dedicated to supporting a vast array of causes, such as empowering women entrepreneurs, promoting environmental sustainability, or fostering the arts. In the US, many of these foundations operate as 501(c)(3) organizations, which mandate their charitable giving.
Demographic-specific grants
Many grants are specifically designated for businesses owned by individuals from underrepresented groups. These can include:
- Grants for women-owned businesses
- Minority-owned business grants
- Grants for veterans
- Grants for entrepreneurs with disabilities
These programs aim to level the playing field and provide opportunities for a more diverse range of business owners.
Pros and cons of a business grant
While "free money" sounds appealing, business grants come with their own set of advantages and challenges. It's crucial to weigh both before investing time and resources into the application process.
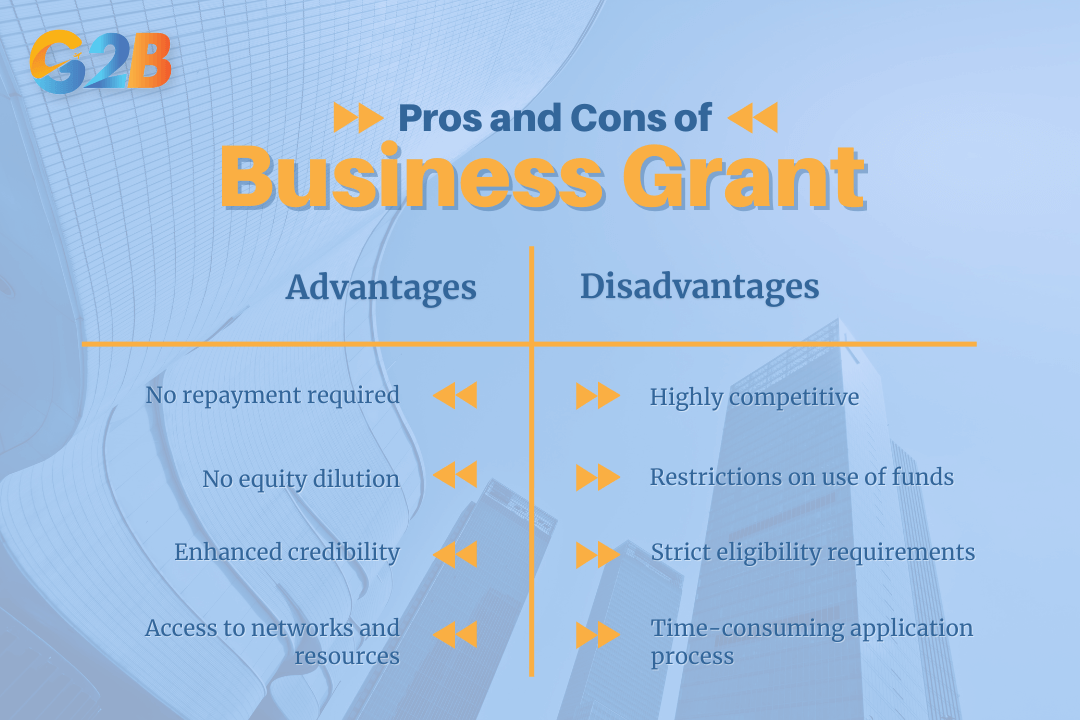
Advantages and disadvantages of a business grant
Advantages
- No repayment required: This is the most significant advantage. The funds you receive do not have to be paid back, which can significantly improve your cash flow and reduce financial risk.
- No equity dilution: You retain full ownership of your company. Unlike seeking investment from venture capitalists or angel investors, you don't have to give up a percentage of your business.
- Enhanced credibility: Winning a prestigious grant can serve as a powerful endorsement of your business idea and your team's capabilities, potentially attracting other investors and partners.
- Access to networks and resources: Some grant programs offer more than just money; they may also provide mentorship, training, and networking opportunities.
Disadvantages
- Highly competitive: Grants attract a large number of applicants, making the selection process incredibly competitive.
- Time-consuming application process: Applying for a grant is a demanding process that requires a detailed proposal, financial documentation, and a well-articulated plan. Some federal grant applications can take over 100 hours to complete. Applicants must often submit a comprehensive business plan and sometimes a detailed feasibility study to prove the viability of their project.
- Strict eligibility requirements: Grants often have very specific criteria related to your industry, location, business size, or the demographics of the ownership. Startups are often excluded from grant support until they have been trading for a couple of years.
- Restrictions on use of funds: The grant money is typically earmarked for specific purposes outlined in your proposal, and you'll be required to report on how it's spent. You can't use the funds for just any business expense.
Key differences between a business grant and a business loan
To make the best choice for your business, it's crucial to understand the fundamental differences between a grant and a loan. While both provide capital, their structures, requirements, and impact on your business are vastly different.
| Feature | Business Grant | Business Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Repayment | Does not require repayment. It is essentially free money for a specific purpose. | Must be repaid over a set period, with interest. |
| Source | Governments, corporations, foundations, or trusts. | Banks, credit unions, online lenders, and government-backed programs (typically a financial institution). |
| Eligibility | Based on meeting specific criteria, such as industry, mission, or demographic. | Primarily based on creditworthiness, financial history, and ability to repay. |
| Use of Funds | Usually restricted to a specific project or purpose outlined in the application. | Generally flexible, allowing for use in various business operations. |
| Competitiveness | Highly competitive, with many businesses vying for a limited pool of funds. | Less competitive in the sense that if you meet the criteria, you are likely to be approved. |
| Impact on Credit | Does not impact your credit score or create debt. | Creates a debt obligation and can affect your business credit score. |
Government grant programs for businesses in Vietnam
As part of its strategy to become a high-tech hub, the Vietnamese government has introduced significant initiatives to attract investment in key sectors. A prime example of this is the establishment of the Investment Support Fund (ISF).
On December 31, 2024, the Vietnamese Government issued Decree No. 182/2024/ND-CP, establishing the Investment Support Fund. This decree took effect from the fiscal year 2024 and applies retroactively to eligible projects registered from that year onward. This decree is a landmark initiative designed to foster innovation and attract high-tech businesses to Vietnam through financial support in the form of cash grants and subsidies. The fund is managed by the Ministry of Planning and Investment and operates as a non-profit, public service unit attached to the Ministry.
Objective
The primary goal of the ISF is to bolster Vietnam's position in the global high-tech landscape, with a particular focus on the semiconductor and artificial intelligence (AI) industries. The fund aims to encourage investment in research and development (R&D) and the manufacturing of high-tech products.
Eligible recipients
The support from the ISF is targeted at:
- High-tech enterprises.
- Businesses with investment projects in high-tech product manufacturing.
- Enterprises with high-tech application projects.
- Companies investing in R&D centers.
This is particularly relevant for investors considering green field investment policies in Vietnam, where setting up new R&D facilities from scratch can qualify for substantial support.
Types of support offered
The ISF provides two main categories of financial support:
- Support for initial investment costs: Enterprises that invest in R&D centers in strategic sectors like semiconductors and AI can receive support of up to 50% of the project's initial investment costs.
- Annual support for actual costs: This support covers a percentage of the actual expenses incurred during a fiscal year for specific activities. The support levels vary:
- Up to 50% of actual costs for human resource development and training for Vietnamese employees.
- Progressive rates for R&D expenses:
- 20-30% for high-tech enterprises and those with high-tech application projects.
- 10-20% for enterprises investing in R&D centers.
- 1-10% for companies with high-tech product manufacturing projects.
Key eligibility criteria
To qualify for support, businesses generally need to meet specific criteria related to minimum capital investment, annual revenue, or employment targets. For example, high-tech projects may require a minimum capital investment of VND 12,000 billion or generate annual revenue of at least VND 20,000 billion. However, there are exceptions for critical industries like microchip design, which may be exempt from capital requirements but must meet targets for employing and training Vietnamese engineers. The establishment of the Investment Support Fund signals a strong commitment from the Vietnamese government to create a favorable environment for high-tech investment and innovation.
Securing a business grant is a challenging yet rewarding endeavor that can provide the capital your business needs to grow without the burden of debt. From government programs to corporate initiatives, a multitude of opportunities exist for those willing to navigate the competitive landscape. While the application process demands thorough preparation and a compelling proposal, the payoff of receiving non-repayable, non-dilutive funding is immense. For businesses operating in or considering expansion into Vietnam, the new Investment Support Fund presents a unique and timely opportunity to gain a competitive edge in the high-tech sector. Whether you are a local startup or a multinational corporation, exploring grant funding is a strategic move that can accelerate your journey to success. For expert guidance on company formation in Vietnam, G2B is here to support your journey.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
