A feasibility study is a critical assessment of the practicality and viability of a proposed project or business venture. This essential preliminary step helps businesses and project managers determine if an idea is worth the investment of time, money, and resources before committing to a full-scale launch. Let’s discover its core definition, various types of feasibility assessments, a detailed process, and the immense benefits.
This article outlines the key components of a feasibility study to help businesses gain a clearer understanding of its scope and practical applications. We specialize in company formation and do not provide economic or investment advice. For specific financial, technical, or operational matters, please consult a qualified legal, financial, or industry expert.
What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study is an in-depth analysis that evaluates the viability and practicality of a proposed project or business plan. This analytical tool is used to rationally determine if a venture is likely to succeed by examining all critical factors, such as the economic, technical, legal, and operational, market, financial, organizational, and environmental aspects. The primary objective is to provide decision-makers comprehensive and reliable data necessary to make informed choices, minimize risks, and assess the project's overall ability to be successfully implemented, whether to proceed, redesign, or cancel a project altogether.
Before significant capital is invested, a feasibility study provides a clear and objective picture of the potential hurdles and the required resources. It scrutinizes the project's potential return on investment (ROI), identifies risks, and ensures that the proposed plan aligns with the organization's strategic goals. Essentially, it answers the fundamental question: “Is this project feasible?” by thoroughly assessing if the expected benefits justify the costs and risks involved.
How many types of feasibility studies?
To gain a comprehensive understanding of a project's viability, a feasibility study typically examines several key facets. A study assesses multiple factors, such as technical capabilities, financial viability, market demand, and legal compliance. While these components are often interconnected, they are usually analyzed as distinct types of feasibility studies to ensure a thorough evaluation.
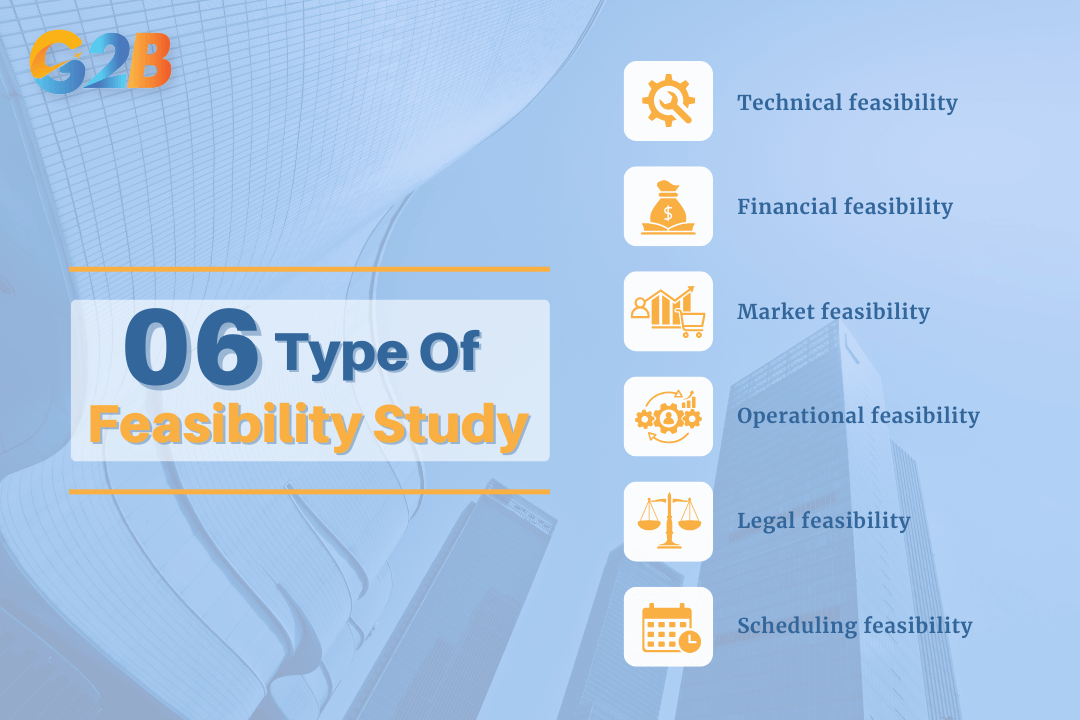
There are six primary types of feasibility studies
Technical feasibility
This assessment centers on the technical resources available to the organization. It determines whether the company has the necessary hardware, software, and technical expertise to complete the project successfully. Key questions addressed include whether the current technology can support the new project, if the technical team has the right skills, and if the proposed system can be integrated with existing infrastructure. For example, a project would be deemed technically infeasible if it required technology that is not yet developed or accessible.
Financial feasibility
This is a detailed evaluation that includes cost-benefit analysis as well as the project’s financial sustainability, funding sources, and financial risk assessment. It involves a detailed estimation of all costs, including initial investment, operational costs, and potential unforeseen expenses, and weighs them against the projected revenue and benefits. The goal is to determine the project's financial viability and whether it will deliver a positive return on investment (ROI). This study includes elements like projected income statements, cash flow analysis, and identifying sources of funding. It helps stakeholders understand if the project is worth the financial risk.
Market feasibility
A market feasibility study evaluates the potential for a product or service in the marketplace. It involves a thorough analysis of the industry, target audience, competition, market size, and projected sales. This research helps to determine if there is sufficient consumer demand to make the project a success. It answers critical questions about market saturation, customer preferences, and effective marketing strategies, ensuring that the project aligns with a real-world need.
Operational feasibility
This study assesses how well the project integrates with the organization's existing and proposed operations. It analyzes whether the business's organizational structure, management, staffing, and internal processes can support the project's completion and long-term success. Essentially, it determines if the company can reliably execute the project. Key considerations include resource availability, compatibility with current systems, and the impact on daily workflows.
Legal feasibility
The legal feasibility study investigates whether any aspect of the proposed project conflicts with legal requirements. This includes zoning laws, data protection regulations (like GDPR), tax obligations, and any necessary permits or licenses. The goal is to ensure that the project can be developed and operated without violating any local or national laws, thereby avoiding potential legal disputes, penalties, and liabilities that could jeopardize the venture.
Scheduling (or time) feasibility
This type of assessment evaluates the project's proposed timeline. It analyzes whether the project can be completed within a reasonable and specified timeframe. A project that takes too long to complete might miss its window of opportunity or become obsolete. This study involves estimating the duration of each task, identifying dependencies, and creating a realistic project schedule to determine if the deadlines are achievable. It ensures the overall timeline aligns with project goals and external constraints.
Feasibility study process
Conducting a thorough feasibility study is a structured process that involves several critical steps. Following this sequence ensures that all aspects of the proposed project are systematically evaluated, leading to a well-founded and reliable conclusion. The process provides decision-makers with a clear path from initial idea to a final "go" or "no-go" decision. Here is a detailed, step-by-step guide:
- Conduct a preliminary analysis: The first step is to perform a high-level preliminary analysis to screen the project idea. This involves outlining the project plan and objectives in broad strokes. The purpose is to identify any obvious flaws or insurmountable obstacles before investing significant time and resources into a more detailed study. This phase often involves consultations with key stakeholders to gather initial feedback and identify major red flags. This step is critical for reducing risks and avoiding unnecessary expenditure early in the process. If the idea seems fundamentally flawed from the outset, the process can be halted early, saving valuable resources.
- Define the scope of the study: Once the preliminary analysis suggests the idea has merit, the next step is to define the scope of the full feasibility study clearly. For example, if you plan to register a company in Vietnam, the study should cover legal compliance, market demand, financial requirements, and operational readiness. This involves establishing the boundaries of the analysis, identifying the key areas to be investigated (e.g., technical, financial, market), and setting clear objectives for what the study aims to achieve. A well-defined scope ensures that the research remains focused and that all critical questions are addressed, preventing the study from becoming too broad or overlooking essential details.
- Conduct a market survey: This is often one of the most crucial parts of the feasibility process. A thorough market survey or market research is conducted to assess the potential demand for the product or service. This step involves analyzing the target market, identifying customer demographics and preferences, and evaluating the competitive landscape. Methods used can include customer surveys, interviews with industry experts, and analysis of existing market data. The goal is to determine if a viable market exists and to forecast potential sales volume. A crucial part of this process is the market survey. For a deeper dive, explore our comprehensive market research services.
- Assess financial and operational viability: In this phase, you crunch the numbers and evaluate the internal capabilities of the organization. The financial assessment involves creating a projected income statement, estimating all start-up and operational costs, and forecasting potential revenue and profit margins. It also includes cash flow analysis to ensure liquidity and financial stability over time. This provides a clear picture of the project's financial feasibility and its potential return on investment. Simultaneously, the operational assessment looks at the business's organizational structure and determines if the existing resources, such as staffing, equipment, and technology, are sufficient to execute the project. It identifies any gaps that need to be filled through hiring, training, or acquisition.
- Identify potential roadblocks and alternatives: No project is without risks. This step involves a critical review to identify potential roadblocks, vulnerabilities, and challenges that could hinder the project's success. These can be internal constraints, such as a lack of skilled personnel, or external threats, like a new competitor entering the market. Once risks are identified, the team should brainstorm alternative solutions and develop contingency plans. This is an essential part of risk management, ensuring the project is prepared for potential setbacks with effective mitigation strategies.
- Review and analyze all data: With all the information gathered from the previous steps, the next stage is to consolidate and analyze the findings. This involves a holistic review of the market research, financial projections, technical assessments, and operational plans. Decision-makers must critically evaluate all the data to ensure it is consistent, accurate, and provides a clear picture of the project's overall feasibility. This step often requires comparing different scenarios and weighing the pros and cons of moving forward.
- Prepare and present the feasibility report: The findings, analyses, and recommendations are compiled into a formal feasibility report. This report clearly presents the evidence supporting the feasibility or infeasibility of the project, outlines any risks, and suggests the recommended course of action. It serves as a key decision-making document and communication tool for stakeholders and management for the next project phase.
- Make a go/no-go decision: The final step in the process is to make a formal recommendation based on the study's findings. This conclusion, typically presented in a feasibility report, summarizes the key data and provides a clear "go" or "no-go" decision. If the project is deemed feasible, the recommendation will outline the proposed course of action and next steps. If it's not feasible, the report will explain the reasoning and may suggest alternative projects or modifications. This final decision is the culmination of the entire process, providing stakeholders with the confidence to either commit resources or avoid a potentially costly mistake.
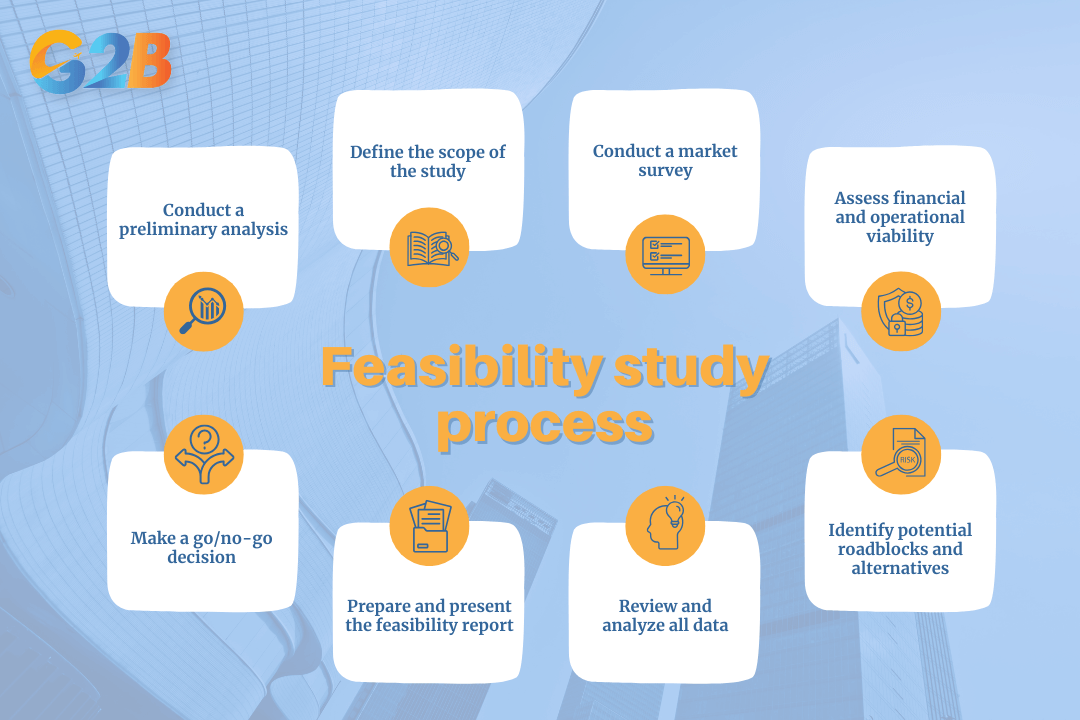
Conducting a thorough feasibility study involves several critical steps
Key components of a feasibility study report
The findings of a feasibility study are compiled into a comprehensive report. This document serves as the primary tool for stakeholders to understand the project's viability and make an informed decision. The structure and content of the report are designed to present the analysis in a clear, logical, and persuasive manner. The most critical component is often the Executive Summary, as it provides a high-level overview for stakeholders.
Here are the key components typically found in a feasibility study report:
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the entire report, highlighting the project's description, the key findings of the study, and the final recommendation. It is designed for busy executives and stakeholders who may not read the entire document.
- Description of product/service: This section provides a detailed description of the product, service, or project being proposed. It explains what it is, what it does, and the problem it solves for the target audience.
- Technological considerations: This component outlines all the technical aspects of the project. It details the technology and equipment needed, the technical expertise required, and how the proposed solution will be developed and implemented.
- Market analysis: This section presents the findings from the market research. It includes a description of the target market, an analysis of the industry and competition, and projections for market demand and sales.
- Marketing strategy: Based on the market analysis, this part of the report describes the proposed strategy for reaching the target audience. It covers aspects such as pricing, distribution channels, and promotional activities.
- Operational feasibility: This section details how the business will be structured and managed to support the project. It includes information on staffing needs, organizational structure, and the operational processes required for execution.
- Project schedule: A detailed timeline for the project is presented here. This includes key milestones, deadlines for major tasks, and the projected completion date.
- Financial projections: This critical section contains all the financial data, including the projected startup costs, operating expenses, revenue forecasts, and a cost-benefit analysis. It provides a clear picture of the project's financial viability and potential profitability. It also typically includes sensitivity analysis, cash flow projections, and sources of financing.
- Findings and recommendations: This concluding section summarizes the study's overall findings. It explicitly states whether the project is considered feasible and provides a clear "go" or "no-go" recommendation, along with the rationale based on the comprehensive analysis presented in the report.
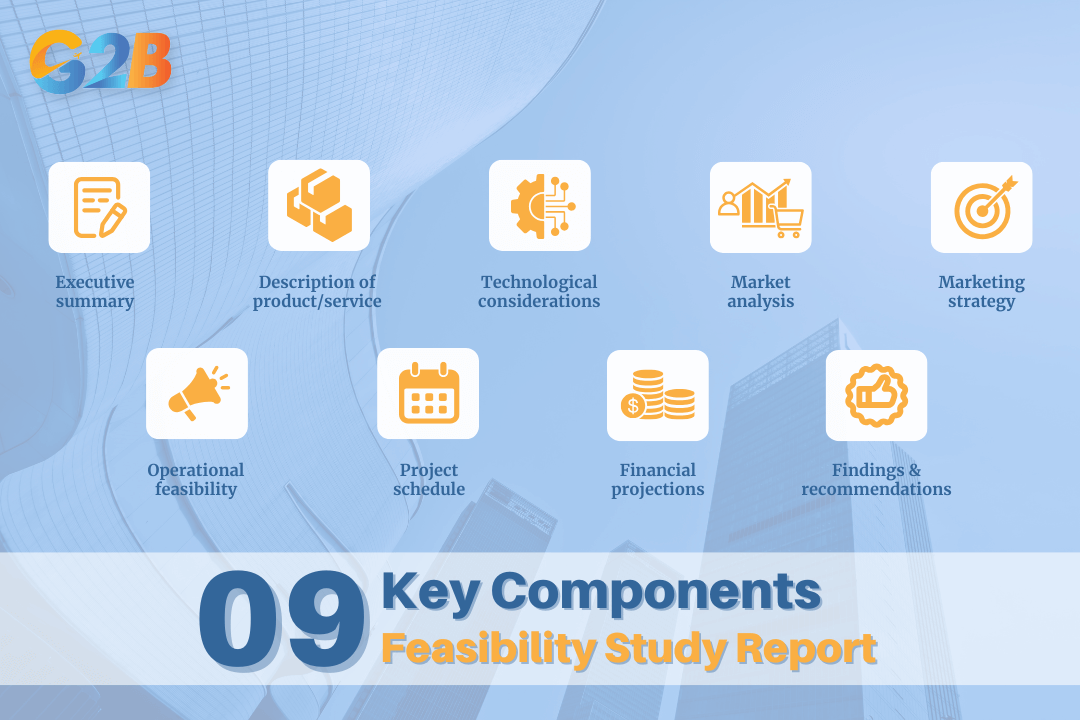
There are several key components typically found in a feasibility study report
Importance and benefits of a feasibility study
Conducting a feasibility study is a crucial preliminary step that provides numerous benefits and strategic advantages. It is an investment that can save a company from wasting significant time and money on a venture destined to fail. By systematically vetting an idea, a feasibility study provides the critical data necessary for informed project investment decisions.
Here are some of the key importance and benefits:
- Informed decision-making: A feasibility study provides stakeholders with comprehensive, data-driven insights, enabling them to make well-informed decisions about whether to proceed with a project.
- Risk identification and mitigation: It helps identify potential risks, challenges, and constraints early in the project lifecycle, allowing teams to develop proactive strategies to minimize their impact.
- Investor and stakeholder attraction: A detailed and positive feasibility report can be a powerful tool for attracting investors and securing funding. It demonstrates due diligence and provides evidence of the project's potential for success.
- Resource optimization: The study evaluates the resources required for a project, ensuring they are allocated and utilized efficiently and effectively. This prevents over-commitment of resources to unviable ideas.
- Improved project focus: By clarifying the project's scope and objectives, a feasibility study helps to improve the project team's focus and provides a clear roadmap for execution.
- Identification of new opportunities: The in-depth analysis conducted during a feasibility study can often uncover new ideas or opportunities that might have otherwise been overlooked.
A feasibility study is an indispensable tool in modern project management and business development. It serves as a crucial checkpoint, ensuring that ideas are thoroughly vetted before significant resources are committed. By systematically evaluating a project from every critical angle - from technical and financial to market and operational - a feasibility study provides the clarity and confidence needed to make strategic, data-driven decisions. It not only helps in identifying and mitigating potential risks but also uncovers new opportunities, ultimately increasing the likelihood of a project's success.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
