An emerging market economy is a developing nation undergoing rapid economic growth and integration into the global system. As developed markets become increasingly saturated, entrepreneurs and investors are turning their attention to these dynamic, high-potential economies for expansion and diversification. These markets represent not just new frontiers for business but a fundamental shift in the global economic landscape.
This article explores the opportunities and challenges of emerging market economies, providing businesses with a clearer perspective on their potential growth and inherent risks. We specialize in company formation and do not provide financial advice. For financial matters, please consult a qualified legal or financial expert.
What is an emerging market economy?
Understanding the precise definition and classification of emerging markets is the first step for any investor or business looking to tap into their growth potential. These economies are in a state of transition, possessing a unique blend of characteristics that set them apart from both developing and developed nations.
Definition and core characteristics
An emerging market economy is transitioning from a low-income, often pre-industrial stage, to a modern, industrial economy with a higher standard of living. They are characterized by a set of distinct traits that signal their growth trajectory and integration with global markets. Key characteristics include:
- Rapid GDP growth: Emerging economies frequently experience faster GDP growth compared to their developed counterparts, often in the range of 6% to 7% annually. This growth is typically fueled by significant industrialization and investments in infrastructure.
- Transition to an open economy: These nations are actively moving from closed, centrally planned systems to more open, market-based economies, encouraging foreign direct investment (FDI) and international trade, and implementing institutional reforms to improve market transparency and legal frameworks.
- Expanding middle class: Economic improvements lead to a rising middle class with increased disposable income, creating a robust and growing consumer base.
- High production and lower labor costs: Labor is often available at a lower cost, which stimulates production, increases employment, and attracts manufacturing and outsourcing from developed countries.
- Volatility and instability: While offering high growth potential, emerging markets are also susceptible to greater volatility. They can be vulnerable to shifts in commodity prices, currency fluctuations, and political instability, and weaknesses in governance and financial systems.
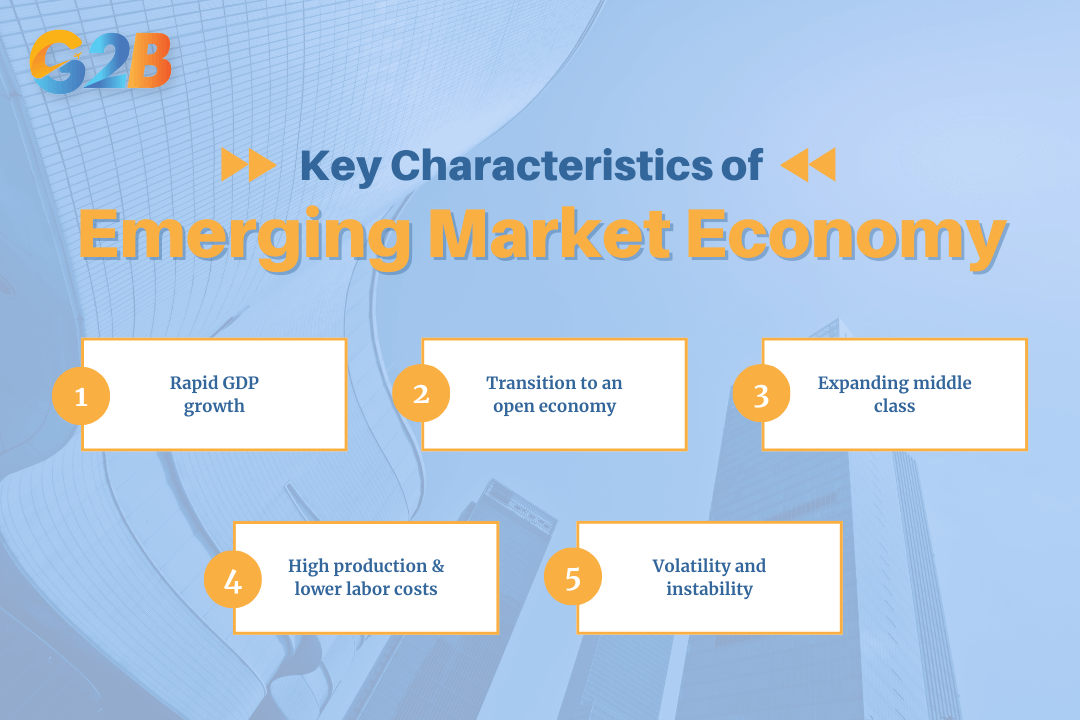
Key characteristics of an emerging market economy
How are emerging markets classified?
The classification of a country as an emerging market is determined by various global financial institutions and index providers, each with its own criteria. Three of the most influential are:
- MSCI (Morgan stanley capital international): The MSCI Emerging Markets Index is a benchmark widely used by global investors. MSCI classifies markets based on criteria such as a country's economic development, market size and liquidity, market accessibility and openness to foreign investors, and institutional frameworks.
- FTSE russell: The FTSE Emerging Index is another key benchmark. FTSE's classification system also considers factors like the quality of the regulatory environment, the development of the financial system, and the ease of capital flows.
- World bank: The World Bank categorizes countries by income levels (low, lower-middle, upper-middle, and high). Countries with low- to middle-per capita income that are undergoing rapid industrialization and economic development are generally considered emerging economies.
It is also important to distinguish between different tiers of developing economies. A frontier market is a developing country that is even less established than an emerging market, often with smaller, riskier, or more illiquid capital markets. Over time, as a frontier market develops and meets the necessary criteria, it can be upgraded to emerging market status.
Top emerging market economies in 2024
Below is a survey of promising markets, establishing a broad authority before narrowing our focus. Emerging Asia is projected to see the highest real GDP growth in 2024 at 5.2%.
Asia-Pacific: The growth engine
- India: With its vast population, strong domestic demand, and a burgeoning digital ecosystem, India is a high-potential market. The government's focus on manufacturing incentives and infrastructure development continues to attract significant foreign investment.
- Indonesia: As Southeast Asia's largest economy, Indonesia's booming e-commerce sector and young, tech-savvy population present massive opportunities. Its wealth of natural resources also makes it a key player in global supply chains.
- Vietnam: Positioned as a prime manufacturing hub for supply chain diversification, Vietnam's stable government, strategic trade agreements, and consistent high GDP, key components of the overall Vietnam economic growth, make it a top destination for FDI.
Latin America: Nearshoring and resources
- Mexico: Benefiting from the nearshoring trend, Mexico's proximity to the U.S. market makes it a strategic manufacturing and logistics hub. Its established industrial base is a major draw for companies looking to de-risk their supply chains.
- Brazil: As the region's largest economy, Brazil's strengths lie in its vast agricultural sector, natural resources, and a growing consumer market. Monetary policy shifts in Brazil can now influence foreign exchange markets and inflation expectations primarily in Latin America and among commodity-exporting countries.
Africa: The digital frontier
- Nigeria: With the continent's largest population and a dynamic fintech scene, Nigeria is at the forefront of Africa's digital transformation. Its young, entrepreneurial population is driving innovation in financial services and e-commerce, while the oil and gas sector remains a critical economic pillar.
Eastern Europe & Central Asia: Tech and resilience
- Poland: A leader in the IT outsourcing and business services sector, Poland boasts a highly skilled workforce and a strategic location within the European Union. Its resilient economy continues to attract tech and manufacturing investments.
Comparison table: Top 10 emerging markets at a glance (2024)*
| Country | Region | 2024 Est. GDP Growth | Key Sector(s) | Primary Opportunity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| India | Asia-Pacific | 6.5% | IT, Manufacturing, Services | Digital ecosystem, domestic demand |
| Vietnam | Asia-Pacific | 6.1% | Manufacturing, Exports, Tech | Supply chain diversification |
| Indonesia | Asia-Pacific | 5.0% | E-commerce, Natural Resources | Young consumer market |
| Mexico | Latin America | 2.5% | Manufacturing, Automotive | Nearshoring to U.S. market |
| Brazil | Latin America | 2.2% | Agriculture, Commodities | Large domestic market |
| Poland | Eastern Europe | 3.0% | IT Outsourcing, Manufacturing | Skilled workforce, EU access |
| Nigeria | Africa | 3.1% | Fintech, Oil & Gas, Services | Digital finance innovation |
| South Africa | Africa | 1.0% | Mining, Finance, Tourism | Advanced infrastructure |
| Thailand | Asia-Pacific | 3.8% | Tourism, Automotive, Health | Regional travel hub, medical tourism |
| Malaysia | Asia-Pacific | 4.3% | Electronics, Palm Oil, Services | High-tech manufacturing |
*Data compiled from various economic forecasts for 2024
Vietnam - A strategic gateway in Asia’s emerging market boom
Vietnam has firmly established itself as one of the most dynamic and attractive emerging economies, not just in Southeast Asia but globally. Its unique combination of economic resilience, strategic location, and business-friendly policies makes it a compelling case study for successful market entry.
Why Vietnam stands out
- Consistent high GDP growth: Vietnam has a proven track record of robust economic performance, with the World Bank forecasting its economy to grow by 7.09% in 2024. This consistent growth demonstrates a resilient and expanding economy capable of weathering global uncertainties.
- Strategic location and manufacturing hub: Situated in the heart of ASEAN and sharing a border with China, Vietnam is a critical hub for regional and global supply chains. It has become a premier destination for companies pursuing a "China+1" strategy to diversify their manufacturing bases.
- Extensive network of free trade agreements (FTAs): Vietnam's integration into the global economy is supercharged by a series of major trade agreements, such as the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA), the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). These agreements reduce tariffs, open market access, and create a more predictable trade environment for foreign investors.
Business-friendly reforms
The Vietnamese government has actively worked to improve its investment climate and attract foreign capital. Policies have been implemented to streamline administrative procedures, enhance transparency, and open more sectors to foreign investment. In many industries, it is now possible to establish a 100% foreign-owned enterprise, giving investors full control over their operations.
Common entry paths for foreign investors
Investors have several legal structures to choose from when entering Vietnam, each suited to different business objectives:
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): The most popular choice for foreign investors, an LLC can be either 100% foreign-owned or a joint venture with a Vietnamese partner. It offers flexibility and limits the liability of its owners to their capital contribution.
- Joint-Stock Company (JSC): A JSC requires at least three shareholders and is the only structure that can issue shares to the public. It is suitable for larger-scale investments or companies planning to list on the stock exchange.
- Branch Office: A branch office is a dependent entity of a foreign parent company and is permitted to conduct commercial activities within Vietnam. This structure is typically used by businesses in specific sectors like banking and finance.
- Representative Office (RO): An RO is the simplest form of presence. It cannot conduct profit-generating activities but can be used for market research, sourcing, and liaising with local partners.
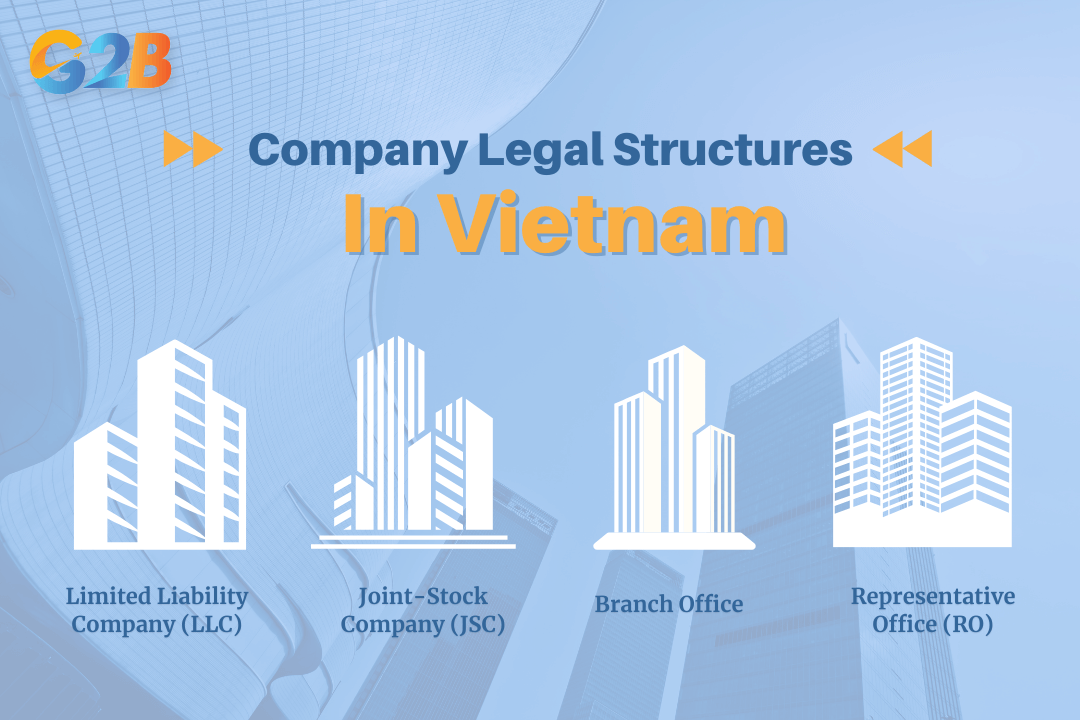
Several legal structures to choose from when entering Vietnam
Why do you need a local incorporation partner in Vietnam?
Successfully establishing a business in Vietnam requires navigating a multi-step process to obtain recognition as a legal entity and ensure full compliance with local regulations. This process involves:
- Language barriers: All official documents must be in Vietnamese.
- Complex paperwork: The application dossiers for the IRC and ERC require meticulous preparation, including proof of financial capacity and legal status.
- Navigating local authorities: Liaising with the Department of Planning and Investment and other government bodies requires local expertise.
How to successfully enter an emerging market: A step-by-step framework
Entering any new market requires a structured, methodical approach. This five-step framework provides a clear roadmap for businesses to plan and execute their expansion into an emerging economy, minimizing risks and maximizing the chances of success.
Step 1: Conduct in-depth market research
Before committing any resources, conduct thorough research to validate your opportunity. This includes analyzing the economic growth, population demographics, competitive landscape, and regulatory environment of your target market.
Step 2: Develop a localized market entry strategy
Choose an entry mode that aligns with your business goals and risk appetite. Common strategies include exporting, forming a joint venture with a local company, licensing or franchising, or establishing a wholly-owned subsidiary through foreign direct investment (FDI). Adapting your products, services, and marketing to local cultural norms is critical for success.
Step 3: Choose the right legal structure
Select the most appropriate legal entity for your operations. This decision will impact your liability, tax obligations, and level of control. In many markets, options include a Limited Liability Company (LLC), a Joint-Stock Company (JSC), a branch, or a representative office.
Explore the pros and cons of each business structure in our complete guide
Step 4: Navigate the company registration process
This is the most complex phase and involves securing the necessary approvals and licenses from government authorities. In a market like Vietnam, this means obtaining the Investment Registration Certificate (IRC) followed by the Enterprise Registration Certificate (ERC). Each step requires precise documentation and adherence to local laws.
Step 5: Ensure post-incorporation compliance
Once your company is registered, the work isn't over. You must immediately address post-incorporation tasks to remain compliant. This includes opening a corporate bank account, contributing charter capital within the legal timeframe, registering for taxes, creating a company seal, and setting up compliant accounting and HR systems.
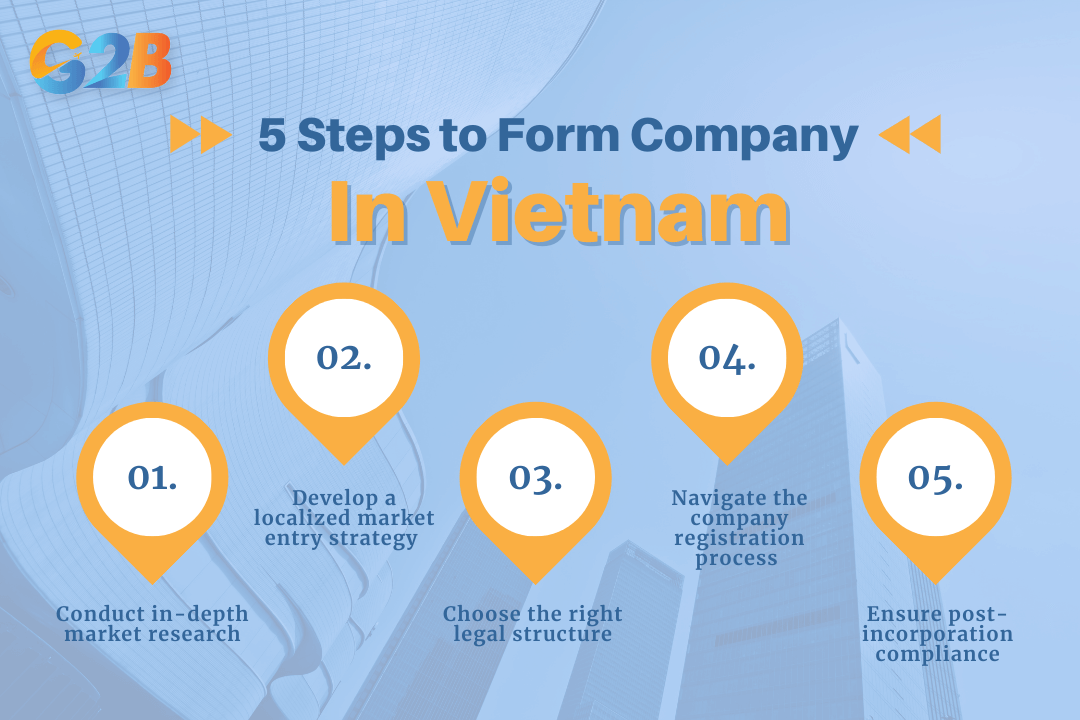
This five-step framework provides a clear roadmap for businesses to enter Vietnam
Emerging market economies present the most significant growth opportunities in today's global business landscape. From the manufacturing powerhouses of Asia to the digital innovators in Africa and the nearshoring hubs in Latin America, these dynamic regions offer a path to expansion, diversification, and higher returns. However, the immense reward is balanced by unique risks and regulatory complexities. Success is not just about having a great product or service; it's about navigating the entry process with precision and expertise.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
