Entrepreneurs are widely recognized as key drivers of innovation, economic growth, and social transformation in modern societies. By creating businesses, generating employment, and introducing new solutions, they play an essential role in shaping sustainable development. Beyond financial contributions, entrepreneurs influence cultural shifts, technological progress, and community well-being. Understanding who entrepreneurs are and how they contribute to social development provides valuable insights into their broader impact on society.
Who are entrepreneurs?
An entrepreneur is an individual who initiates, organizes, and manages a business venture, often assuming the majority of the risks and rewarding benefits involved. This process, known as entrepreneurship, encompasses not only the creation of new businesses but also the innovation and development of existing enterprises and business models.
Entrepreneurs are widely recognized as innovators who introduce new ideas, products, services, and strategies to the market, driving economic growth and addressing societal needs. They are individuals who identify opportunities, mobilize resources, and take the initiative to turn their vision into reality, frequently solving problems for profit. The term applies to a diverse spectrum of people, from small business owners supporting their families to founders of large-scale, disruptive companies that transform entire industries.
Main roles of entrepreneurs in the economy and society
Entrepreneurs are crucial drivers of economic growth and social change. Their contributions are diverse and have a significant impact.
Economic roles
- Job creation: By establishing new businesses, entrepreneurs create job opportunities for themselves and others, which is critical for reducing unemployment. When an entrepreneur starts a business, they not only create a position for themselves but also provide jobs for many other job seekers. These new and existing businesses are one of the fundamental goals of economic development.
- Driving innovation and competition: Entrepreneurs introduce new technologies, products, and services, stimulating innovation and challenging existing companies to become more competitive and efficient. This process of "creative destruction" replaces inferior innovations and drives economic progress. Entrepreneurs bring radical or incremental innovations adapted to local market needs, making a significant contribution to economic advancement.
- Wealth creation: They mobilize their own resources and attract capital, leading to the creation and distribution of wealth within the economy. By establishing a business entity, entrepreneurs invest their own resources and attract capital from investors, lenders, and the public. Successful business ventures also contribute to national income and generate tax revenue.
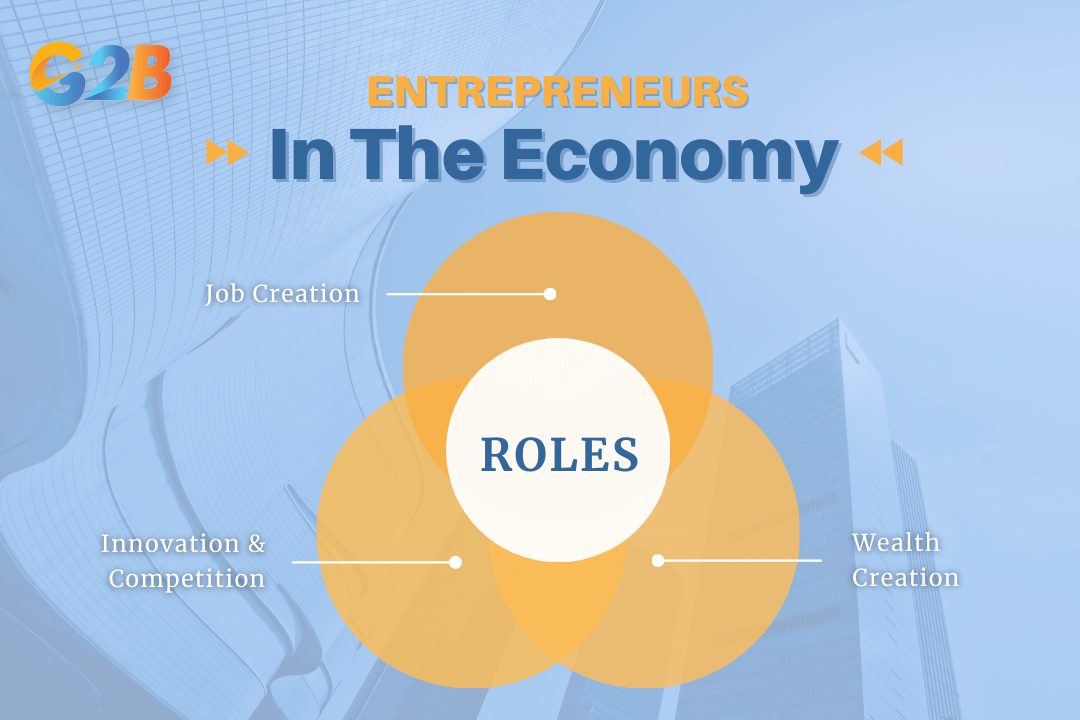
There are 3 main roles of entrepreneurs in the economy
Social roles
- Improving standard of living: Entrepreneurs contribute to a higher standard of living by creating jobs and developing innovations that improve the quality of life for employees and consumers. For example, automation that helps reduce production costs and allows for faster production will make a business unit more efficient, while also providing customers with similar products at a lower price.
- Driving social change: They can act as agents of social change by introducing new ideas and improving how people live and work. Social entrepreneurs, in particular, focus on creating business ventures to solve pressing social and environmental issues.
- Community development: Successful entrepreneurs often contribute to community development through philanthropy, such as donating to education and other social causes. Through their involvement in Corporate Social Responsibility, entrepreneurs contribute and support the development of infrastructure for education, healthcare, and other social needs.
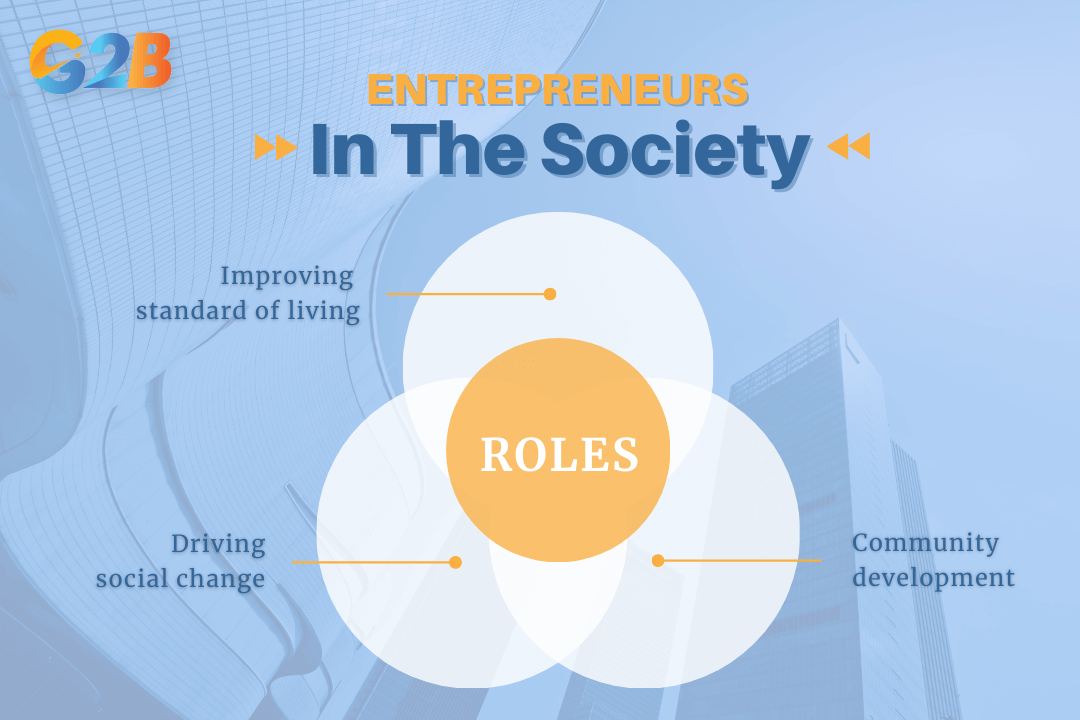
There are 3 main roles of entrepreneurs in society
How many types of entrepreneurs are there?
The concept of an entrepreneur is not a one-size-fits-all model. It can be categorized in various ways, often based on the goals and structure of the business.
- Small business entrepreneurship: This type involves starting a business, like a local shop or service provider, without the primary goal of turning it into a large conglomerate or franchise. The owner often invests their own money.
- Scalable startup entrepreneurship: These entrepreneurs start with an idea they believe can change the world. They focus on creating a repeatable and scalable business model, often seeking venture capital to fuel rapid growth.
- Large company entrepreneurship (Intrapreneurship): This involves developing a new business division or project within an existing large company. The organization uses its resources to expand into new markets or technologies.
- Social entrepreneurship: Social entrepreneurs create businesses with the primary goal of making a positive impact on society. They aim to solve social or environmental problems while remaining financially sustainable.
- Innovative entrepreneurship: These entrepreneurs focus on creating groundbreaking ideas, products, or services that can disrupt traditional business models and industries.
- Imitative entrepreneurship: Imitators take existing successful business ideas and improve upon them with their own modifications or adjustments.
- Buyer entrepreneurship: These entrepreneurs often have previous business success and look to acquire promising existing businesses rather than starting from scratch.
Challenges and benefits of entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is a journey marked by both significant opportunities and formidable obstacles, requiring vision, adaptability, and persistence. Understanding the challenges and benefits of entrepreneurship provides valuable insight into how business leaders navigate uncertainty while creating lasting economic and social impact.
Entrepreneurship has significant opportunities and formidable obstacles
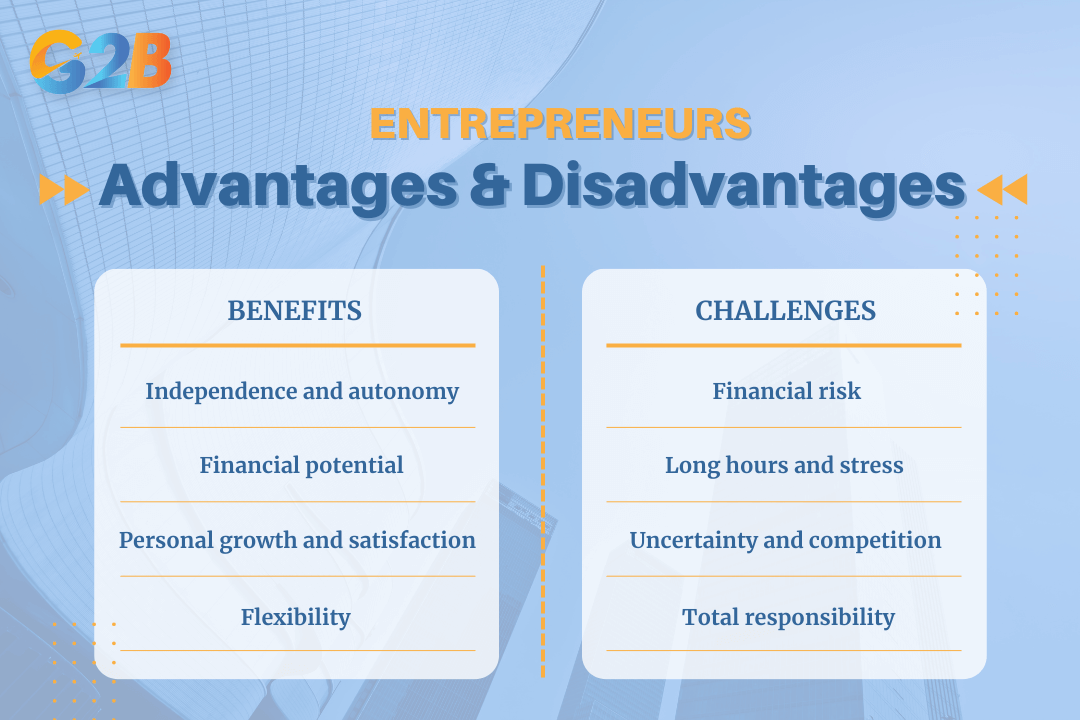
Benefits
- Independence and autonomy: The ability to be your own boss, set your own schedule, and control the direction of the company is a primary motivator.
- Financial potential: Although risky, successful entrepreneurship can lead to significant financial success and wealth.
- Personal growth and satisfaction: This journey offers many opportunities for learning and personal development. There is a deep sense of accomplishment in building something from scratch.
- Flexibility: Being an entrepreneur can offer a more flexible work-life balance, although it often requires long hours initially.
Challenges
- Financial risk: Entrepreneurs often invest their own money and face the possibility of failure and financial loss. Income volatility is one of the biggest challenges.
- Long hours and stress: The responsibility of running a business often leads to extended work hours and significant stress, which can affect mental health. Many small business owners work more than 60 hours per week.
- Uncertainty and competition: The business environment is unpredictable, and entrepreneurs must constantly deal with market competition and adapt to change.
- Total responsibility: The ultimate success or failure of the business rests on the entrepreneur's shoulders, which can be a heavy burden.
Entrepreneur transcends the simple definition of a business owner. It represents a dynamic force of innovation, resilience, and progress that is fundamental to the architecture of our modern economy and society. Entrepreneurs are the catalysts for economic vitality - creating jobs, spurring competition, and generating wealth. From groundbreaking startups to initiatives like company formation in Vietnam, their ventures demonstrate how entrepreneurship shapes industries, strengthens communities, and accelerates national development. Beyond the balance sheets, their influence extends deep into the social fabric, driving change, enhancing standards of living, and fostering community growth.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
