In today’s competitive business landscape, mastering supply chain management is not just an asset - it's a necessity. Faced with escalating operational costs and complex logistics challenges, business leaders must navigate a myriad of factors to ensure streamlined operations. Moreover, incorporating a business in Delaware offers distinct legal and financial benefits, which can provide a strong foundation for optimizing operations, including supply chain management.
This article is provided for general informational purposes to help new business owners and decision-makers better understand the fundamentals of supply chain management. We are specialists in the field of company formation, not providing consulting or advisory services related to logistics or operational workflows. Therefore, this information should not be considered professional supply chain advice. Please consult a qualified supply chain consultant or business operations advisor for tailored recommendations.
What is supply chain management?
Supply chain management (SCM) is the coordinated management of the flow of goods, services, information, and finances as a product or service moves from the procurement of raw materials to its final delivery to the customer. SCM encompasses every stage involved in getting a product from its initial concept to the end consumer, including sourcing, manufacturing, inventory management, logistics, and distribution.
5 core aspects of supply chain management:
- Planning: Forecasting demand, managing inventory, and setting strategies to ensure products meet customer needs while optimizing costs and efficiency.
- Sourcing: Selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing supplier relationships to secure raw materials and components reliably.
- Manufacturing: Overseeing production processes, quality control, and inventory management to convert raw materials into finished goods.
- Delivery: Managing logistics, warehousing, transportation, and distribution to ensure products reach customers on time and in good condition.
- Returns: Handling the reverse flow of goods, including returns, recycling, and disposal, while maintaining customer satisfaction and quality standards.
Importance of supply chain management for business success
Supply chain management (SCM) is important for business because it directly impacts cost efficiency, customer satisfaction, risk management, and competitive advantage, whether you're a startup forming a legal entity such as an LLC or a large corporation.
1. Cost reduction and efficiency
Effective supply chain management helps businesses reduce operational costs by minimizing waste, optimizing transportation routes, and improving inventory management. Companies can cut supply chain expenses significantly - studies suggest 5-15% savings with well-run SCM - by streamlining procurement, production, and logistics processes. This leads to better profit margins and improved cash flow.
2. Improved customer satisfaction
A well-managed supply chain ensures that products are available in the right quantity, at the right place, and at the right time. This reliability enhances customer satisfaction by preventing stockouts and delivery delays, which in turn fosters customer loyalty and repeat business. Efficient SCM also enables rapid response to changing customer demands, maintaining service quality in competitive markets.
3. Inventory optimization
SCM helps maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing excess stock and storage costs while avoiding shortages. This balance improves resource utilization and profitability by aligning production and supply with actual market demand.
4. Faster time to market and competitive advantage
Streamlined supply chains enable companies to launch new products more quickly and respond agilely to market changes. This agility provides a competitive edge by meeting customer needs faster and more effectively than competitors.
5. Risk mitigation and business resilience
Supply chain management identifies and manages risks such as supplier disruptions, transportation delays, and regulatory compliance issues. By diversifying suppliers, developing contingency plans, and monitoring supply chain performance, businesses can minimize operational disruptions and protect their reputation.
6. Strategic importance and business growth
SCM is increasingly recognized as a core business function essential for growth and sustainability. It supports better decision-making, resource allocation, and innovation, helping companies expand their market share and enhance profitability.
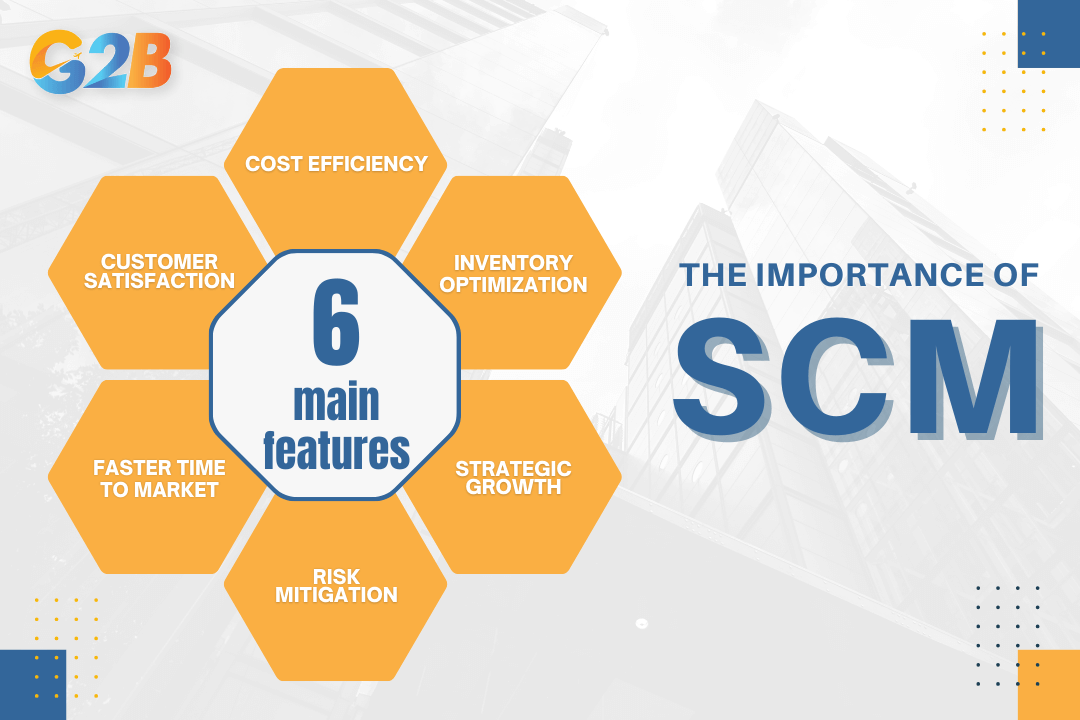
The importance of supply chain management for business success
5 key components of supply chain management
The success of modern businesses heavily relies on the efficient management of their supply chains. Understanding the key components of supply chain management (SCM) is necessary to streamline operations and ensure a competitive advantage:
1. Procurement processes
Procurement is the initial step in the supply chain journey. It involves acquiring goods and services from external sources. The effectiveness of the procurement process significantly impacts the overall supply chain performance. Procurement is not just about purchasing but involves a strategic approach to acquiring the right goods at the right price and ensuring timely delivery. This component requires businesses to establish clear procurement strategies, engage in supplier negotiations, and manage contracts effectively.
2. Inventory control
Inventory control is a pivotal component in managing a successful supply chain. It focuses on optimizing inventory levels to meet customer demands without incurring excess costs or stockouts. Effective inventory management involves monitoring inventory levels, forecasting demand accurately, and implementing inventory reduction strategies such as Just-In-Time (JIT) and reorder point planning. With advancements in technology, businesses are now adopting AI-driven inventory systems to predict demand more accurately and automate reorder processes.
3. Logistics and distribution networks
Logistics and distribution networks are critical in ensuring that goods move efficiently from the point of origin to the point of consumption. This component encompasses transportation management, warehousing, and order fulfilment. Efficient logistics management ensures timely delivery and high customer satisfaction while minimizing transportation costs. Businesses must design flexible distribution networks that can adapt to market changes and disruptions. The strategic placement of warehouses and the selection of optimal transportation methods play a crucial role in achieving operational efficiency.
4. Supplier relationship management
The relationships a business fosters with its suppliers can drastically affect supply chain performance. Effective supplier relationship management (SRM) involves building strong, collaborative partnerships that can withstand operational disruption. By maintaining open communication channels and implementing performance evaluations, businesses can work closely with suppliers to improve product quality, reduce costs, and ensure timely deliveries. SRM strategies may include setting clear performance metrics, conducting regular supplier audits, and engaging in joint planning and development initiatives.
5. Transportation management
Transportation management is a complex element in the supply chain, focusing on the efficient movement of goods between locations. It involves planning, executing, and optimizing the physical transport of products. This component requires businesses to manage various transportation modes and routes and negotiate with carriers to reduce transportation costs. Implementing transportation management systems (TMS) can facilitate route optimization, load consolidation, and freight auditing, further enhancing efficiency.
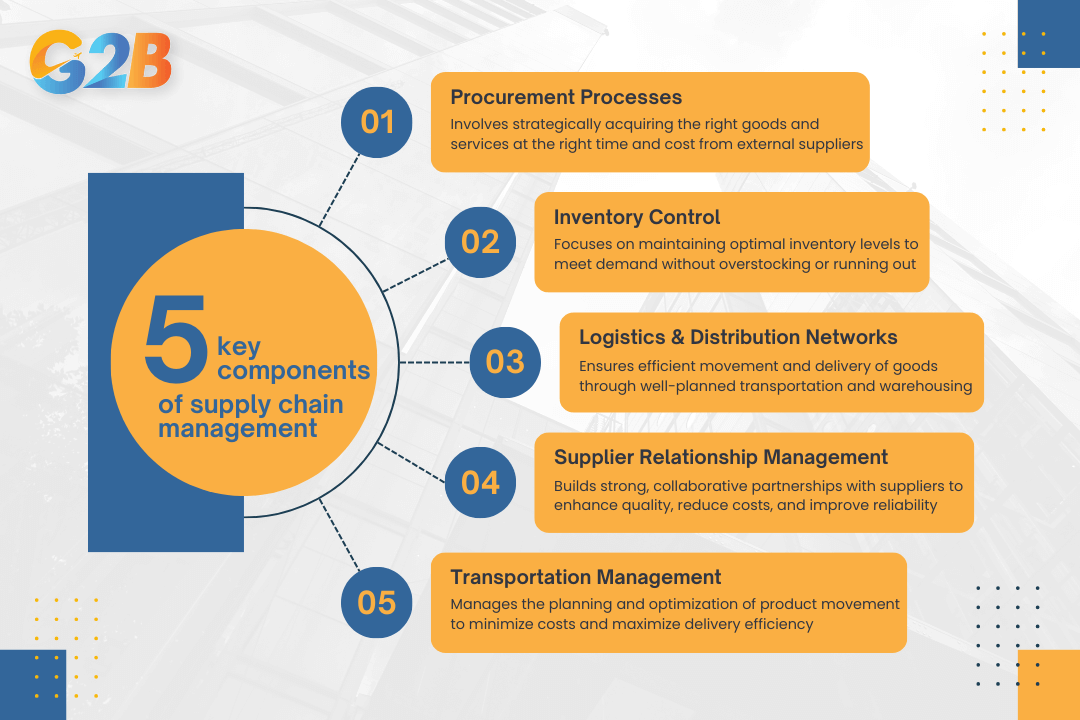
There are 5 key components of supply chain management
Strategies for effective supply chain management
Effective supply chain management is vital for businesses seeking to achieve cost-efficiency, reliable delivery, and customer satisfaction. Implementing well-structured strategies can lead to significant performance improvements.
Lean management principles
Lean management principles focus on minimizing waste and maximizing value in supply chain processes. By eliminating non-value-added activities, companies can streamline operations and improve efficiency. Some fundamental lean strategies include:
- Value stream mapping: This involves analyzing the flow of materials and information through the supply chain to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks. By visualizing the entire process, businesses can pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Just-in-time (JIT) inventory: JIT approaches help companies reduce inventory costs by aligning production schedules closely with customer demand. This reduces excess stock and storage expenses, allowing more resource allocation towards value-added activities.
- Kaizen (Continuous improvement): Emphasizing small, incremental changes, Kaizen encourages employees at all levels to propose process enhancements. This cultural shift towards constant refinement leads to sustainable performance improvements over time.
Risk mitigation techniques
Supply chain disruptions, whether from geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or supplier failures, can severely impact business operations. Risk mitigation strategies prepare businesses to handle uncertainties effectively:
- Diversification of suppliers: Relying on multiple suppliers for critical components reduces dependency on any single source, mitigating risks linked to individual supplier failures or regional disruptions.
- Scenario analysis and contingency planning: Conducting thorough scenario analysis allows businesses to anticipate potential risks and establish contingency plans, ensuring quick response and recovery when disruptions occur.
- Insurance and contractual safeguards: Insurance policies and well-defined contracts with suppliers can provide financial protection and clarity during unforeseen events, reducing the impact of disruptions on business continuity.
Cost reduction methods
Cost reduction is a primary objective of supply chain management. Implementing effective methods can lead to substantial savings:
- Strategic sourcing: By optimizing procurement strategies and negotiating better terms with suppliers, businesses can reduce material costs and improve margins.
- Automation of routine processes: Technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can handle repetitive tasks such as invoicing and order processing, reducing labor costs and minimizing human errors.
- Energy efficiency initiatives: Investing in energy-efficient logistics operations and sustainable transportation options not only decreases costs but also aligns with growing corporate responsibility expectations.
Continuous improvement processes
Continuous improvement is vital for maintaining a competitive edge in dynamic markets. Businesses should focus on:
- Performance metrics and data analytics: Utilizing advanced data analytics tools to monitor supply chain performance enables the timely identification of issues and opportunities for improvement.
- Feedback loops and customer engagement: Regularly collecting and analyzing customer feedback helps businesses align their supply chain strategies with changing market needs, ensuring ongoing relevance and customer satisfaction.
- Innovation and technology adoption: Embracing new technologies such as AI and IoT can enhance operational efficiency and provide insights for optimizing supply chain elements, from inventory management to demand forecasting.
Enhancing supplier collaboration
Building robust relationships with suppliers fosters collaboration and mutual growth. Effective supplier collaboration involves:
- Joint development initiatives: Collaborating with suppliers on product development or process improvements can lead to innovation and competitive advantages for both parties.
- Transparent communication channels: Establishing clear and open communication ensures that all parties are aligned on objectives, expectations, and changes in demand or supply conditions.
- Long-term partnerships: Developing strategic, long-term partnerships with key suppliers creates stability and reduces uncertainties, providing a foundation for collaborative planning and joint problem-solving.
Technology solutions in supply chain management
This part will explore some of the most critical technology solutions that are revolutionizing supply chain processes.
Role of ERP and SCM software
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Supply Chain Management (SCM) software are essential components in modern supply chain management. They provide a centralized platform that integrates various business processes, from procurement and inventory management to logistics and distribution.
- Centralization and integration: ERP systems offer a consolidated view of business operations, ensuring seamless integration across departments. This integration helps in maintaining a consistent data flow, reducing inefficiencies.
- Real-time data access: SCM software provides real-time insights into various supply chain processes, enabling better demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and resource planning.
- Cost efficiency: By streamlining operations, both ERP and SCM software help in reducing operational costs.
IoT applications in supply chain
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a transformative force within supply chains, enabling businesses to gain unprecedented visibility and control over their operations.
- Enhanced tracking and monitoring: IoT devices, such as sensors and GPS trackers, provide real-time tracking of goods throughout the supply chain. This capability allows for precise monitoring of shipments, reducing the risk of loss or damage.
- Predictive maintenance: IoT-enabled equipment can predict potential malfunctions, facilitating proactive maintenance. This predictive approach minimizes downtime and enhances operational efficiency.
- Inventory management: IoT technology allows for automated inventory tracking, enabling businesses to optimize stock levels and reduce excess inventory, ultimately saving costs.
AI and machine learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are pivotal in driving decision-making processes and enhancing supply chain resilience.
- Demand forecasting: AI algorithms analyze historical data to predict future demand trends, ensuring accurate inventory stocking and reducing the likelihood of stockouts or overstock situations.
- Automated decision making: Machine learning models can automate routine decision-making processes, such as reorder triggers and supplier selection, based on defined criteria and historical performance.
- Risk management: AI tools identify potential risks and bottlenecks in the supply chain, providing early warnings and enabling businesses to implement corrective measures proactively.
Blockchain technology for transparency
Blockchain technology introduces a new level of transparency and security to supply chains, addressing challenges related to trust and traceability.
- Immutable data records: Blockchain creates tamper-proof records of transactions and shipments, ensuring the authenticity and accuracy of information shared among supply chain partners.
- Enhanced traceability: The decentralized nature of blockchain allows for end-to-end traceability, ensuring that all parties have access to the same information. This transparency is crucial for verifying the origin and authenticity of goods.
- Fraud prevention: By providing an unalterable record of transactions, blockchain mitigates the risk of fraudulent activities, enhancing trust between partners and consumers.
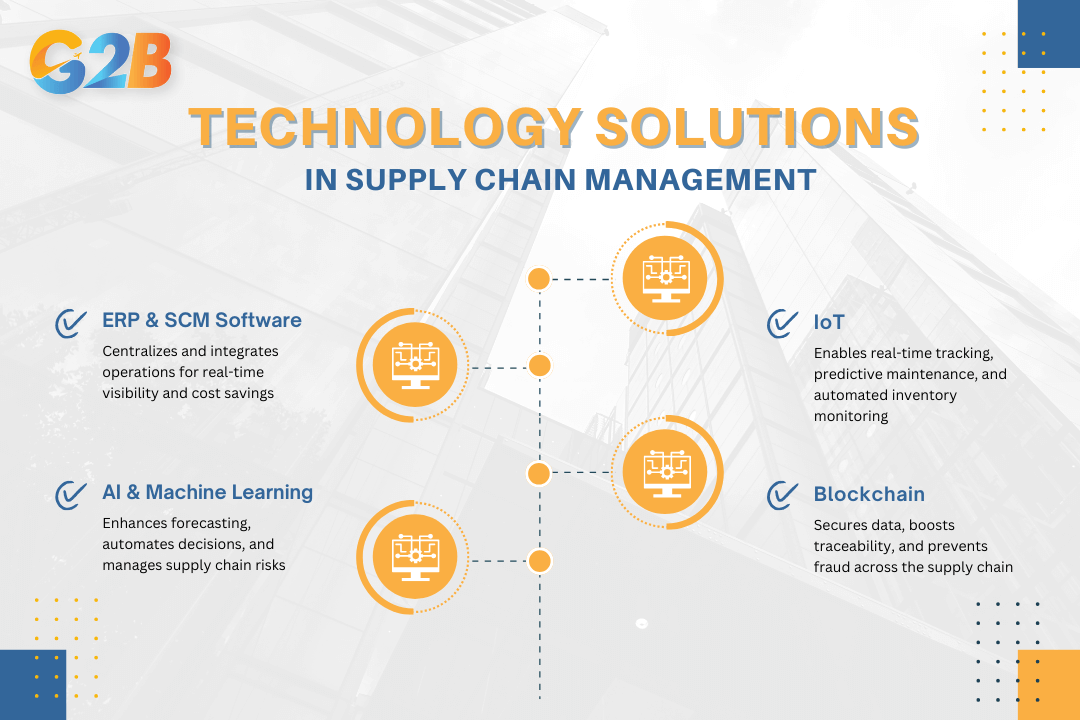
Four of the most critical technology solutions revolutionizing supply chain processes
Common challenges and mitigation strategies
Modern supply chain management is fraught with challenges that can disrupt operations, inflate costs, and diminish service quality. Effectively addressing these challenges is imperative for ensuring smooth business operations.
Overcoming supply chain disruptions
Supply chain disruptions are often unpredictable and can stem from various sources such as natural disasters, geopolitical instability, or pandemics. These disruptions can lead to delays, increased costs, and lost revenues. To mitigate such impacts, businesses should:
- Diversify suppliers: Relying on a single supplier poses significant risks. Companies should develop a diversified supplier base to ensure continuity in case one supplier faces issues.
- Implement robust risk management: Employ predictive analytics and scenario planning to anticipate potential disruptions. Using past data and trend analysis can help in forecasting and preparing for contingencies.
- Enhance communication: Establish transparent channels of communication with all stakeholders, including suppliers and logistics providers, to ensure quick responsiveness and information flow during disruptions.
Tackling global supply chain complexities
As businesses expand globally, supply chains become more complex, involving multiple countries and regulatory requirements. Navigating these complexities requires careful coordination and strategic planning. Strategies include:
- Use of advanced technologies: Technologies such as AI and machine learning can optimize route planning, enhance demand forecasting, and improve inventory management. ERP and SCM software also provide integrated platforms for managing complex operations across borders.
- Localize operations: By establishing local manufacturing or warehousing, businesses can reduce dependency on long international supply chains, minimizing risks associated with cross-border logistics and regulatory adherence.
- Strategic partnerships: Collaborating with local businesses translates into better adaptability to regional markets. It ensures compliance with local regulations and reduces logistical burdens.
Addressing compliance and regulatory issues
Compliance with international trade laws and local regulations is a significant concern for global supply chains. Non-compliance can result in fines, legal battles, or operational halts. Effective mitigation involves:
- Stay updated on regulations: Keeping abreast of changes in international trade laws and regional regulations is crucial. Subscribing to industry regulatory updates and consulting with legal experts ensures proactive compliance management.
- Invest in compliance technologies: Deploying compliance management systems helps automate processes, ensuring that all necessary paperwork and legal requirements are up-to-date and correct.
- Regular training: Conduct regular training sessions for staff on compliance standards and regulatory changes to foster a culture of compliance within the organization.
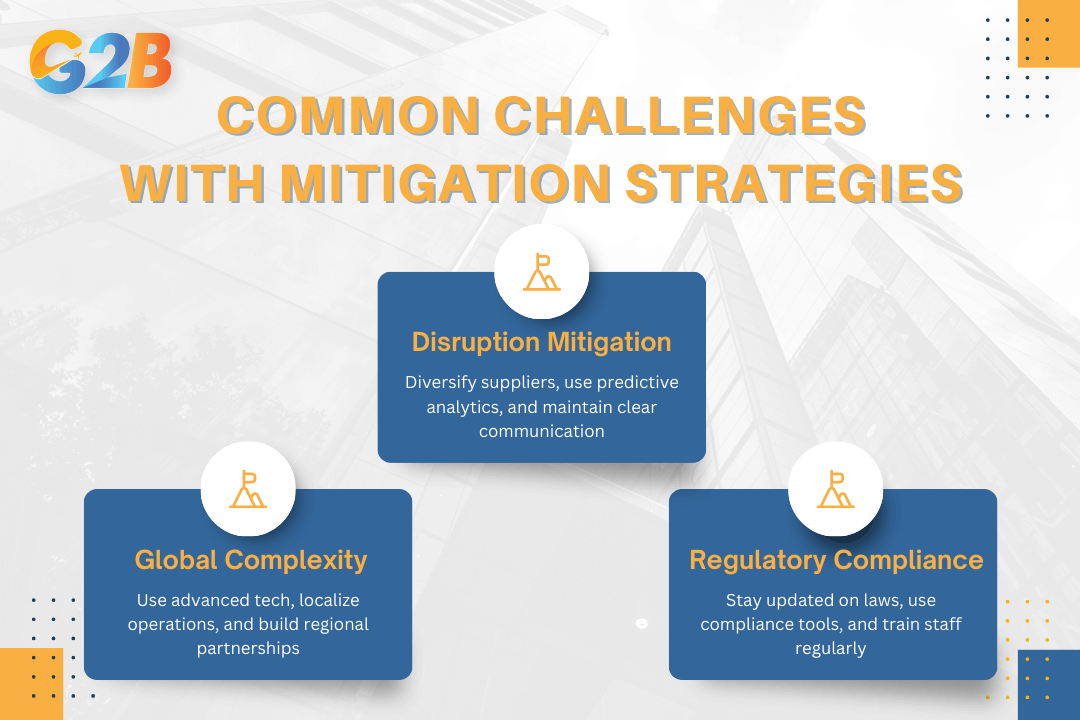
Common challenges and mitigation strategies of supply chain management
How supply chain management reduces business costs
Effective supply chain management is instrumental in reducing business costs. Companies can achieve significant savings and gain a competitive edge by focusing on these key areas.
Improving operational efficiency
Operational efficiency is at the core of cost reduction in supply chain management. By streamlining processes and eliminating bottlenecks, businesses can deliver products faster and more reliably. This involves optimizing logistics and distribution networks, ensuring that transportation methods are both timely and cost-effective.
- Streamlined processes: Emphasizing lean management principles can help in cutting down excess processes. By utilizing ERP and SCM software, businesses can automate tasks, reduce manual errors, and ensure seamless operation from procurement to delivery.
- Data-driven decision making: Employing advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning, businesses can predict demand more accurately and adjust their operations to meet these fluctuations. This reduces the holding costs associated with overproduction or underproduction.
- Enhanced communication: Implementing integrated communication systems across different channels within the supply chain ensures information is relayed quickly and accurately. This reduces delays caused by miscommunication or misinformation.
Reducing waste and redundancy
Reducing waste is crucial not only for cost reduction but also for environmental sustainability. Waste in supply chains often emerges from overproduction, excessive inventory, and inefficient resource utilization.
- Just-in-time inventory: By adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices, companies can significantly cut down on holding costs. This approach ensures products are manufactured based on demand, minimizing excess storage costs and reducing waste of resources.
- Reverse logistics: This involves planning for returns efficiently. Utilizing reverse logistics can help recapture value from returned products through refurbishment or recycling, thus minimizing losses.
- Lean practices: Encouraging lean practices in manufacturing and logistics, such as continuous improvement processes, can help in identifying redundancies and streamlining operations to only the most essential activities.
Optimizing resource allocation
Allocating resources effectively ensures businesses operate with minimal waste, leading to profound cost savings. This involves strategic planning and deployment of human, technological, and capital resources.
- Collaborative forecasting: Working closely with suppliers and vendors using collaborative forecasting techniques helps in better resource planning. This enables businesses to adjust supply levels based on precise demand forecasts, avoiding overstocking or stockouts.
- Efficient use of technology: Integrating IoT devices within the supply chain allows real-time tracking of assets. This visibility helps in optimizing routes for transportation, ensuring energy-efficient and timely deliveries, which ultimately reduces fuel costs and labor hours.
- Skill development: Investing in workforce skill enhancement ensures that employees are versatile and can perform multiple roles effectively. This reduces dependency on hiring additional staff, thereby cutting down labor costs.
Practical steps for small businesses
Small businesses face unique challenges in implementing effective supply chain management due to limitations in resources, budget, and market reach. However, strategic planning and tailored approaches can optimize the supply chain operations.
Tailoring strategies for smaller operations
Small businesses can benefit significantly from customizing supply chain strategies to fit their specific needs and capabilities. A one-size-fits-all approach is rarely effective, particularly for operations with restricted resources. Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your current supply chain processes, identifying areas for improvement and potential bottlenecks. This internal review is critical to developing a focused strategy that aligns with business objectives and customer expectations.
- Focus on agility: Unlike large corporations, small businesses can leverage their size for quicker decision-making and adaptability. Utilize this agility to respond rapidly to market changes, adjusting inventory levels and procurement processes as needed.
- Prioritize key relationships: Establishing strong relationships with a limited number of reliable suppliers can go a long way. By focusing on supplier relationship management, small businesses can negotiate better terms and ensure a steady supply of goods.
- Efficiency through flexibility: Implement flexible work arrangements and multi-skilled workforce policies that allow for cross-functional operations. This flexibility can help in reallocating resources swiftly in response to supply chain disruptions or demand fluctuations.
Leveraging local resources
Leveraging local resources is a powerful strategy for small businesses to enhance supply chain efficiency and reduce costs. Focusing on regional suppliers not only minimizes transportation costs and lead times but also supports local communities and enhances sustainability.
- Choose local suppliers: By sourcing materials locally, businesses can decrease their carbon footprint and foster a community-oriented brand image. Moreover, local suppliers can often offer quicker delivery times, which enhances customer satisfaction.
- Utilize regional logistics providers: Partner with regional logistics companies that understand local market dynamics and can offer tailored solutions for distribution and transportation. Local providers often have better insights and connections that can lead to cost-saving opportunities.
- Engage in community networks: Participating in local business networks can provide insights into industry developments and potential collaborations. Networking can also uncover shared logistics opportunities, allowing multiple businesses to pool resources for transportation or storage.
Cost-effective technology solutions
Investing in technology does not require a massive budget. Small businesses can optimize their supply chains through cost-effective technologies that improve efficiency and decision-making.
- Cloud-based solutions: Cloud technology provides scalable and affordable options for small businesses to manage supply chain operations. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms offer functionalities such as inventory tracking, order management, and real-time data analytics, without the need for significant upfront investments.
- Automation tools: Simple automation tools can streamline repetitive tasks, reducing the need for manual input and minimizing human error. These might include automated order processing systems or digital invoicing, which free up time for strategic activities.
- Data-driven insights: Utilize basic data analytics tools to gain insights into customer preferences, inventory turnover rates, and supplier performance. This data-driven approach aids in making informed decisions, optimizing inventory levels, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
By implementing these practical steps, small businesses can develop a robust supply chain management strategy that is both efficient and sustainable. Tailoring operations to their unique circumstances, harnessing local resources, and adopting cost-effective technologies can create a stronger foundation for growth and competitive advantage. Combining these efforts with an agile mindset will ensure that even small enterprises can thrive in an increasingly complex global market.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
