B2B (Business-to-Business) is a fundamental model of commerce that forms the backbone of the global economy. Unlike B2C (Business-to-Consumer), the B2B landscape involves transactions of goods, services, and data between two or more business entities. Let’s investigate the core B2B meaning, key characteristics, most popular models, advantages and disadvantages in this article.
What is B2B?
B2B (short for "Business-to-Business") is a business model where commercial transactions of goods, services, or information occur between two or more organizations, either directly or through digital/e-commerce platforms. Instead of selling directly to individual consumers, B2B companies provide other businesses with the products and solutions they need to operate, grow, or resell.
This encompasses a vast range of activities, from a manufacturer selling components to an automotive company, to a software firm providing a customer relationship management (CRM) system to a sales team. The core of the B2B meaning is centered on building sustainable partnerships and enabling other businesses' success, thereby playing a critical role in supply chains and economic growth. Establishing a strong B2B presence in Vietnam begins with a solid legal foundation, making it essential to register a company in Vietnam that aligns with the market’s regulatory and commercial landscape.
Key characteristics of the B2B business model
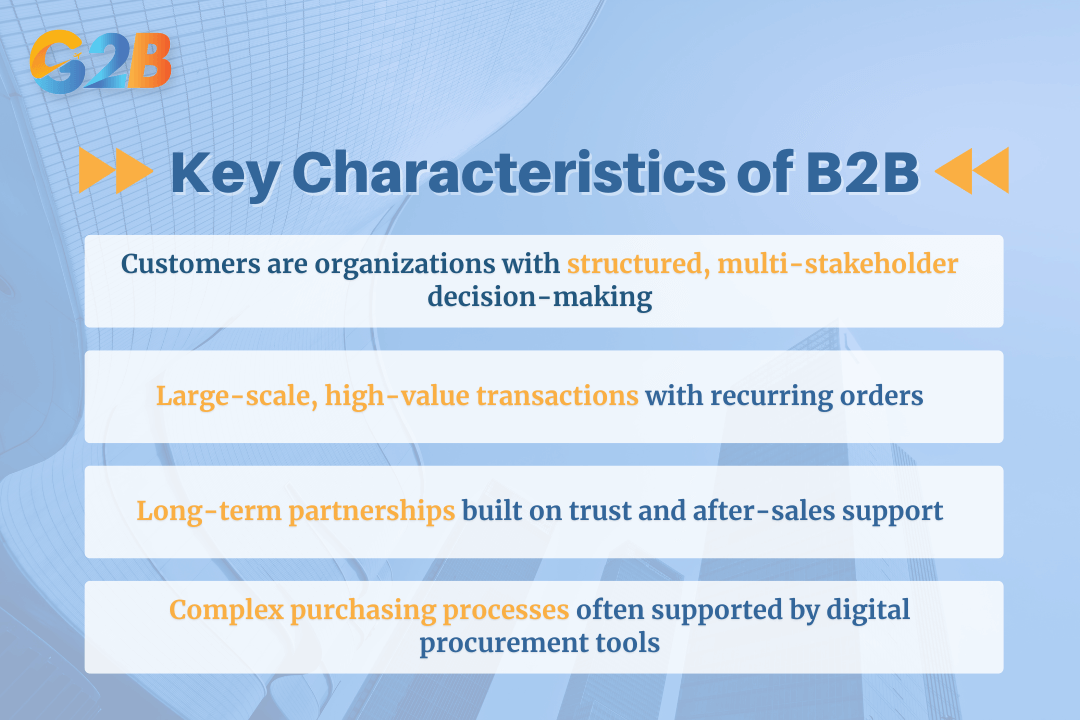
The B2B market operates differently from the consumer market, defined by several distinct characteristics that shape its transactions and relationships. Understanding these features is crucial for any business looking to succeed in this environment.
- Customers are organizations including various types of enterprises from SMEs to large corporations with structured decision-making processes: In the B2B model, the customer is not an individual but a legal entity, such as an entire organization or a representative committee within it. This means purchasing decisions are often driven by logic, return on investment (ROI), and business needs rather than personal emotion. Decision-making involves multiple stakeholders, such as purchasing managers, department heads, and C-level executives.
- Large transaction scale encompassing not only high monetary value but also substantial volumes and recurring orders over long cycles: B2B sales cycles typically involve significantly larger order volumes and higher contract values compared to B2C. A single transaction can be worth thousands or even millions of dollars, as businesses purchase in bulk or invest in high-value capital equipment and enterprise software solutions.
- Long-term relationships with an emphasis on trust, after-sales support, and collaborative development: The B2B model thrives on building and nurturing long-term, strategic partnerships. Due to the complexity and high value of transactions, trust and reliability are of paramount importance. Companies often seek ongoing support, service, and collaboration, making customer retention a primary goal for B2B vendors.
- Complex purchasing process often facilitated by B2B e-commerce platforms and digital procurement tools, increasing efficiency despite inherent complexity: B2B sales cycles typically involve significantly larger order volumes and higher contract values compared to B2C. A single transaction can be worth thousands or even millions of dollars, as businesses purchase in bulk or invest in high-value capital equipment and enterprise software solutions to support their core business activities
Several distinct characteristics shape B2B’s transactions and relationships
Role of the B2B business model
The B2B model is a vital engine of the global economy, playing a multifaceted role that extends far beyond simple commercial exchanges. Its influence is felt across industries, fostering growth, innovation, and strategic alliances that drive the market forward.
- Creating jobs and economic growth: B2B companies are significant employers, creating a wide array of specialized roles in areas like engineering, manufacturing, B2B marketing, and technology, and enhance sustainable economic development by optimizing supply chains and expanding both domestic and international markets. By supplying the necessary tools, materials, and services for other businesses to function and expand, the B2B sector creates a powerful ripple effect that fuels broader economic growth and stability.
- Building strategic partnerships: At its core, business-to-business commerce is about creating symbiotic relationships. B2B transactions often evolve into strategic partnerships, often formalized through long-term contracts and close collaboration to foster mutual growth and competitive advantages. Companies collaborate on product development, share market insights, and align their goals. These alliances create more resilient supply chains and can lead to powerful competitive advantages for all parties involved.
- Enhancing innovation and improvement: The B2B sector is a hotbed of innovation. Businesses constantly demand more efficient, powerful, and cost-effective solutions to solve their operational challenges, leveraging digital platforms and technology to accelerate innovation and operational efficiencies. This pressure drives B2B suppliers to continuously research, develop, and refine their offerings. From advanced enterprise software to cutting-edge industrial machinery, B2B innovation directly enables progress across all other industries.
4 Popular B2B models today
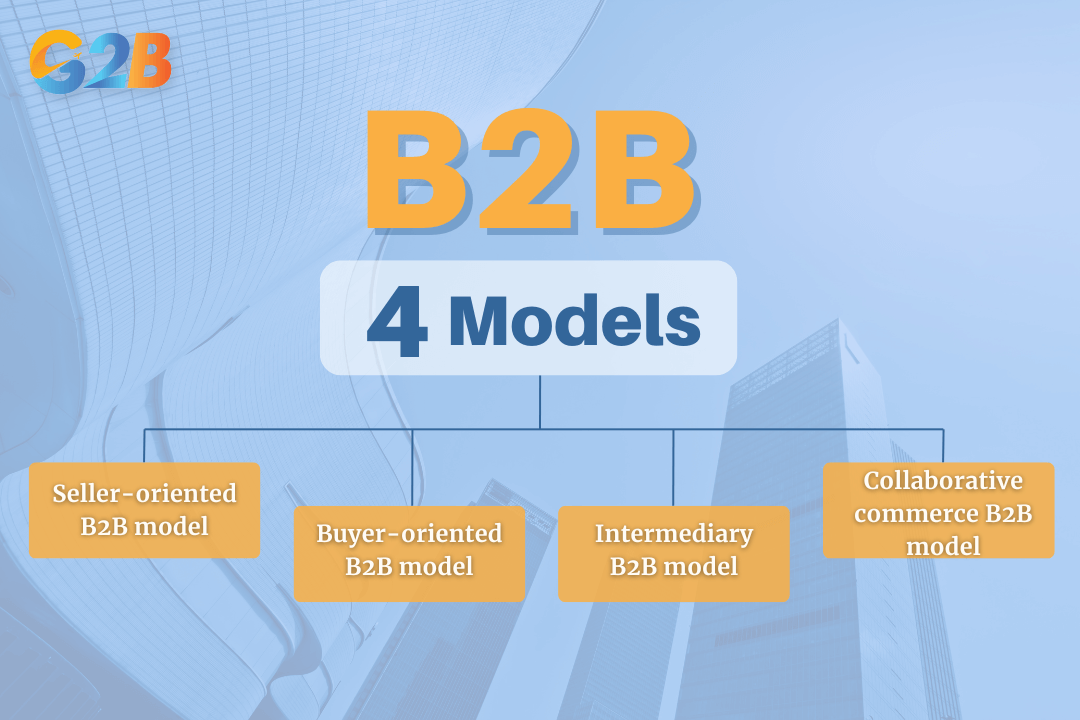
The B2B landscape is not monolithic; it comprises several distinct models that cater to different market dynamics and transactional relationships. Understanding these structures helps clarify how various B2B e-commerce platforms and businesses operate.
- Seller-oriented B2B model: This is the most common model, where a single seller offers its products or services to a multitude of business buyers. The seller typically operates a website or B2B e-commerce platform that serves as a digital catalog for business customers. Companies in sectors like SaaS (Software as a Service), manufacturing, and professional services often use this direct-to-business approach.
- Buyer-oriented B2B model: In this model, the roles are reversed. A large buyer or a group of buyers creates a platform and invites sellers to bid on supplying the required goods or services. This model is common in government procurement and large corporations that need to source significant quantities of materials or services through a competitive bidding process.
- Intermediary B2B model: This model involves a third-party platform that connects multiple buyers and sellers, acting as a neutral marketplace. These intermediaries facilitate transactions by providing a centralized hub for discovering products, comparing prices, and managing orders.
- Collaborative commerce B2B model: This is the most integrated and partnership-focused model. It goes beyond simple transactions to involve deep collaboration between businesses, often within a shared supply chain or on joint projects. This model leverages shared data, integrated systems, and joint planning to improve efficiency, innovate, and achieve mutual business goals.
4 B2B models cater to different market dynamics and transactional relationships
Advantages and disadvantages of the B2B business model
Like any commercial framework, the B2B model presents a unique set of opportunities and challenges. Businesses must carefully weigh these factors to determine if a B2B approach aligns with their strategic goals and capabilities.
Advantages
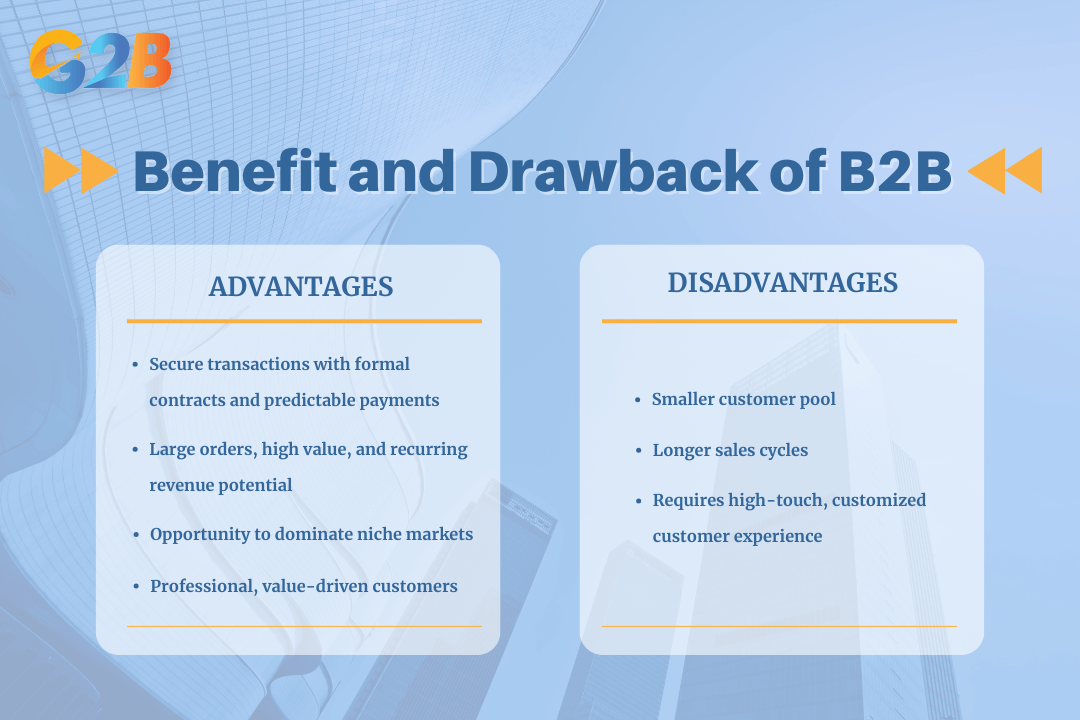
- Safe and secure: B2B transactions are often governed by detailed legal contracts and service level agreements (SLAs), providing a higher degree of security and predictability than consumer sales. Payments are typically handled through formal invoicing and procurement systems, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Large orders, high value, high profits: The scale of B2B transactions is a major draw. Selling in bulk or providing high-value enterprise solutions leads to significantly higher revenue per customer. This allows for greater profit margins and more predictable revenue streams, as many B2B relationships are based on recurring subscriptions or long-term contracts.
- Potential for large market dominance: While the B2B vs B2C market may seem smaller in terms of the number of customers, establishing a strong reputation can lead to significant market share. Becoming the go-to provider in a specific niche or industry can create a powerful competitive moat that is difficult for newcomers to penetrate. The diverse mix of enterprises, including many SMEs, in Vietnam expands the range of opportunities despite a smaller overall customer base.
- Professional customers: Dealing with business clients means interacting with professional buyers who are knowledgeable and focused on value. The sales process is less about emotional appeal and more about a logical, data-driven case for how a product or service can solve a tangible business problem, leading to more rational and productive negotiations.
Disadvantages
- Limited market: The pool of potential customers in the B2B space is inherently smaller than in the consumer market. A company selling specialized industrial equipment will have far fewer potential buyers than one selling smartphones. This makes targeted B2B marketing and effective B2B lead generation absolutely critical for success.
- Prolonged working process: The complexity of B2B needs and the number of stakeholders involved result in a much longer sales cycle. It can take months or even years to close a deal, from initial contact to final contract signing. This requires significant patience, resources, and a dedicated sales team. In Vietnam, this is often further extended by complex internal approval processes and specific business culture practices.
- Different customer experience: The B2B customer journey is fundamentally different. It requires a high-touch, consultative approach with extensive customization, training, and ongoing support. Failing to provide this specialized experience can quickly lead to the loss of a high-value client. The focus is on relationship management rather than transactional volume.
The B2B model presents many advantages and disadvantages
Prominent B2B businesses today
The B2B sector is home to some of the world's largest and most influential companies. These organizations provide the essential infrastructure, platforms, and services that power countless other businesses in the world.
- Amazon business: Leveraging the massive infrastructure of its consumer marketplace, Amazon has built a powerful B2B e-commerce platform called Amazon business. It serves millions of business customers worldwide by providing a streamlined procurement solution with features tailored for organizations, such as business-only pricing, quantity discounts, and tax-exemption programs. The platform also enables sellers to add credentials like "small business" or "ISO 9001 certified" to distinguish themselves. It integrates with procurement systems like SAP Ariba and Oracle NetSuite, offering tools for spend visibility and guided buying to help companies manage their purchasing efficiently.
- Salesforce: A dominant force in the cloud-based software industry, Salesforce provides a comprehensive suite of B2B applications centered around its world-renowned Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform. Its B2B Commerce Cloud is specifically designed to help companies create personalized and efficient online buying experiences for their business customers, handling complexities like bulk ordering, negotiated pricing, and account-specific terms. By centralizing customer data and automating sales processes, Salesforce empowers B2B companies to build stronger relationships, streamline operations, and drive growth.
- IBM: A legacy tech giant that has continually reinvented itself, IBM is a major player in the B2B space, offering a vast portfolio of hardware, software, and consulting services. Its IBM Sterling B2B Collaboration solutions, for example, provide a robust gateway to simplify and automate complex B2B and EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) processes. These tools help companies securely and efficiently exchange data with their partners, manage supply chains, and ensure regulatory compliance. IBM's focus on enterprise-level solutions in areas like hybrid cloud, AI, and cybersecurity makes it a critical partner for many of the world's largest organizations.
Effective marketing strategies for the B2B Model
Marketing in a B2B context requires a different approach than B2C. It's less about mass-market appeal and more about precision, demonstrating value, and building trust with decision-makers over a long sales cycle.
- Website marketing strategy: Your website is your digital storefront and the cornerstone of your B2B marketing. It must be professional, load quickly, and clearly articulate the problems you solve for your customers. Essential pages include a clear homepage explaining your value proposition, detailed product/service pages, and conversion-focused pages like "Request a Demo" or "Talk to an Expert." The site should be optimized for search engines (SEO) to attract qualified prospects actively searching for solutions.
- Content marketing strategy: B2B buyers are information-hungry. Content marketing focuses on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience. This includes blog posts, in-depth white papers, case studies, webinars, and ebooks that address customer pain points and establish your brand as a thought leader. The goal is to educate and build trust, guiding prospects through the buyer's journey.
- Email marketing strategy: Email remains a powerful channel for nurturing leads and maintaining relationships in the B2B space. It allows for direct, personalized communication with prospects and customers. Strategies include automated lead-nurturing sequences that deliver targeted content based on a prospect's behavior, as well as newsletters that share industry insights and company updates to keep your brand top-of-mind.
- Social media communication: While platforms like LinkedIn are the natural home for B2B marketing, other channels like Facebook and Zalo are also effective in Vietnam for showcasing company culture and sharing insights. The key is to focus on platforms where your target audience is most active and share content that provides professional value. B2B social media is about building a community, engaging in industry conversations, and positioning your brand as an expert resource.
Opportunities & Challenges of the B2B Business Model
The B2B sector is a dynamic environment, constantly shaped by technological advancements, market shifts, and evolving customer expectations. Navigating this landscape requires a clear understanding of both the promising opportunities and the significant challenges that lie ahead.
Opportunities
- Revenue growth: The sheer scale of the B2B market presents enormous opportunities for revenue. The global B2B e-commerce market is projected to continue its substantial growth, reaching trillions of dollars. In Vietnam, this growth is accelerated by the rapid adoption of domestic digital platforms and increasing integration into ASEAN and global supply chains. Businesses that can effectively tap into this expanding market have the potential for significant financial success and long-term stability.
- Large market: While the number of individual customers is smaller than in B2C, the B2B market is vast in terms of value and reach. Companies can expand into new geographic regions and industries, leveraging both international digital platforms and emerging local B2B marketplaces to engage in cross-border commerce within Vietnam's dynamic economic zones. This global reach opens up new customer segments and diversifies revenue streams.
- Better partnerships: The B2B model inherently fosters deep, strategic relationships. There is a growing opportunity for businesses to move beyond transactional interactions and build collaborative partnerships. By aligning goals and integrating processes, companies can co-create value, drive innovation, and establish more resilient supply chains.
- Digital technology: Technology is the single biggest driver of opportunity in the B2B space. The adoption of digital tools like AI-powered analytics, automation, and advanced CRM systems is transforming B2B commerce. These technologies enable businesses to streamline operations, gain deeper customer insights, personalize experiences, and make smarter, data-driven decisions, ultimately creating a significant competitive advantage.
Challenges
- Continuous innovation while maintaining customer loyalty: The pace of technological change demands constant innovation. B2B companies face the challenge of continuously updating their products and services to meet evolving client needs. However, they must balance this innovation with the need to maintain stable, reliable service for their existing loyal customers, who may be resistant to frequent changes.
- Professional operations in the Internet environment: As B2B sales and marketing shift online, the expectation for a seamless, professional digital experience has soared. Companies face the challenge of building and maintaining a sophisticated online presence, from an intuitive B2B e-commerce platform to a data-secure, professional brand image. This requires significant investment in technology and skilled digital talent. In Vietnam, building such capabilities is further complicated by a shortage of experienced digital professionals familiar with B2B nuances and local regulatory compliance.
- Managing cash flow and slow payments: The long sales cycles and complex invoicing processes inherent in the B2B model can create significant cash flow challenges. Businesses often face delays in payments from clients, which can strain operational finances. In the Vietnamese context, lengthy administrative procedures and prevalent business culture practices often exacerbate payment delays and complicate cash flow management. Effectively managing accounts receivable, negotiating clear payment terms, and leveraging technology to automate invoicing are critical hurdles to overcome for sustained financial health.
The B2B model is a cornerstone of commerce, defined by transactions between businesses rather than with individual consumers. This fundamental distinction gives rise to its unique characteristics: A focus on professional buyers, large-scale transactions, and the cultivation of long-term, strategic relationships.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
