Starting a business in today's competitive market requires more than just a great idea – it demands a solid understanding of the legal foundations that will support your venture. Among the most critical documents every business owner must understand is the Articles of Incorporation, a fundamental legal document that serves as the cornerstone of corporate existence.
What are Articles of Incorporation?
Articles of Incorporation are a legal document filed with a government agency to establish a corporation as a legal entity formally. This document serves as the official birth certificate of a company, creating its legal existence and enabling it to conduct business operations within the jurisdiction where it's filed.
Purpose of Articles of Incorporation
The primary purpose of the Articles of Incorporation is to define the legal status of the company, allowing the company to operate as a legal entity. This document establishes the corporation's legal existence, separating it from its founders and providing the necessary framework for business operations. By filing these articles, entrepreneurs transform their business concept into a legally protected entity that can engage in commercial activities, enter into binding agreements, and enjoy the benefits of corporate protection under the law.
Roles of Articles of Incorporation
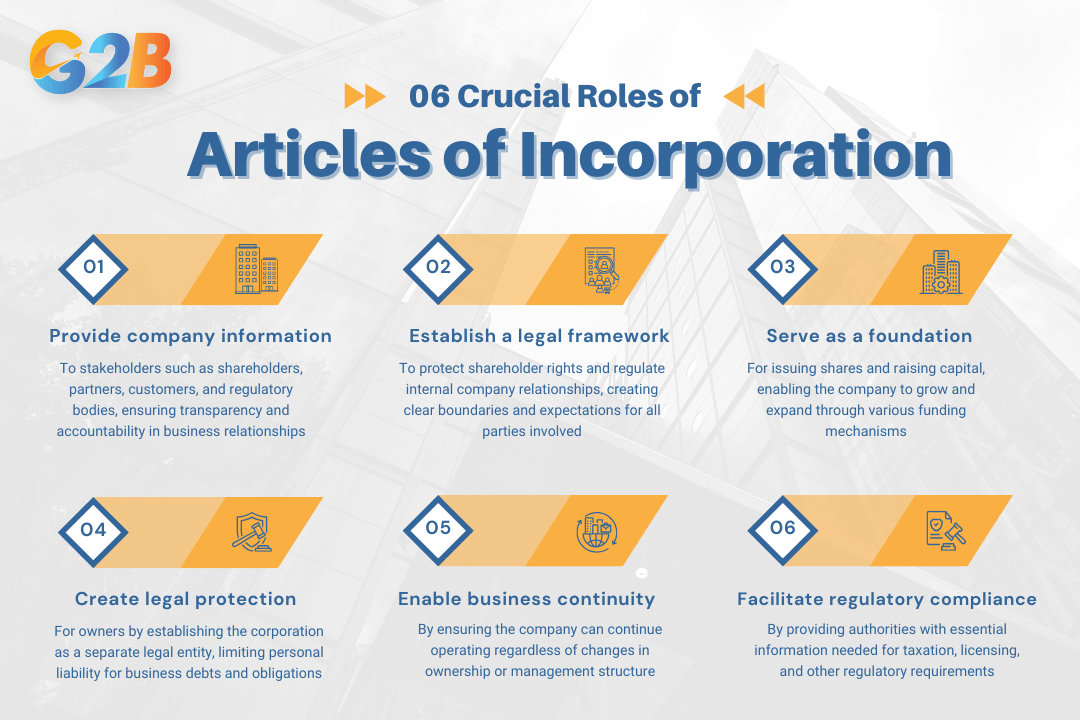
Articles of Incorporation serve several crucial roles in the business ecosystem:
- Provide basic company information to stakeholders such as shareholders, partners, customers, and regulatory bodies, ensuring transparency and accountability in business relationships.
- Establish a legal framework to protect shareholder rights and regulate internal company relationships, creating clear boundaries and expectations for all parties involved.
- Serve as a foundation for issuing shares and raising capital, enabling the company to grow and expand through various funding mechanisms.
- Create legal protection for owners by establishing the corporation as a separate legal entity, limiting personal liability for business debts and obligations.
- Enable business continuity by ensuring the company can continue operating regardless of changes in ownership or management structure.
- Facilitate regulatory compliance by providing authorities with essential information needed for taxation, licensing, and other regulatory requirements.
Articles of Incorporation serve several crucial roles in the business ecosystem
What do Articles of Incorporation include?
The Articles of Incorporation typically contain several essential elements that define the company's structure and operations:
- Company name: The legal name used for business transactions and operations. This name must be unique within the jurisdiction and often includes corporate designations such as "Inc.," or "Corp.”, depending on the business structure chosen.
- Registered office address and registered agent: The official location of the company for communication and conducting business activities. This address serves as the legal point of contact for all official correspondence and legal proceedings, with the registered agent being the person or entity authorized to receive legal documents.
- Business purpose: The scope or field of the company's operation, describing what activities the corporation is authorized to engage in. This section may be broad or specific, depending on the company's strategic plans and regulatory requirements.
- Share structure: The types and number of shares authorized for issuance, including the associated rights. This section outlines the company's capital structure, voting rights, dividend preferences, and other shareholder privileges.
- Incorporator information: Names, addresses, and contact details of the incorporators. This information establishes the initial ownership structure and provides contact information for key stakeholders.
- Information about the Board of Directors or Management (if applicable), including the number of directors, their roles, and any specific qualifications or requirements they must meet.
- Provisions related to shareholder rights and obligations, and company management procedures. These may be referenced or detailed further in the corporate bylaws, but basic governance principles are often outlined in the articles themselves.
- Duration of the corporation: The intended lifespan of the corporation, which can be perpetual or for a fixed term, depending on the filing.
Incorporation process and submission of Articles of Incorporation
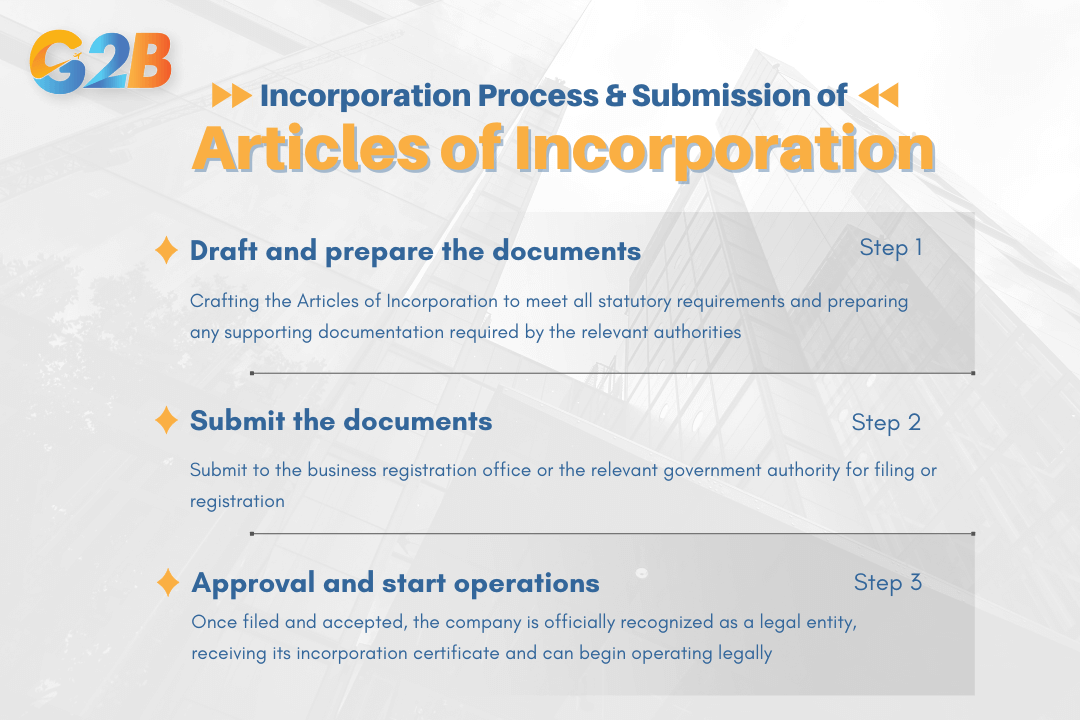
The incorporation process involves several key steps that must be completed accurately to ensure successful business formation:
- Draft and prepare the documents under local legal regulations. This involves carefully crafting the Articles of Incorporation to meet all statutory requirements, ensuring compliance with local laws, and preparing any supporting documentation required by the relevant authorities.
- Submit the documents to the business registration office or the relevant government authority for filing or registration. This step typically involves paying required fees, providing necessary supporting documents, and completing any additional forms required by the jurisdiction.
- Once filed and accepted, the company is officially recognized as a legal entity. Following approval, the business receives its incorporation certificate and can begin operating legally, opening bank accounts, entering into contracts, and conducting business activities under its corporate structure.
The incorporation process involves several key steps that must be completed accurately
Articles of Incorporation vs other legal documents
Understanding how Articles of Incorporation differ from other corporate documents is essential for proper business management and compliance.
1. Articles of Incorporation vs Bylaws
Bylaws are internal documents that outline the detailed governance and operational procedures of the company. Unlike the Articles of Incorporation, bylaws are not publicly filed documents and provide more specific guidance on day-to-day operations, meeting procedures, officer responsibilities, and internal decision-making processes. While Articles of Incorporation establish the company's legal existence, bylaws govern how that company operates internally.
2. Articles of Incorporation vs Operating Agreement
Operating Agreements apply to Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) and are distinct from the Articles of Incorporation, which are used for corporations. Operating Agreements serve a similar function to bylaws but are specifically designed for LLC structures, outlining member rights, profit distribution, management structure, and operational procedures unique to the LLC business model.
Practical importance of Articles of Incorporation in business
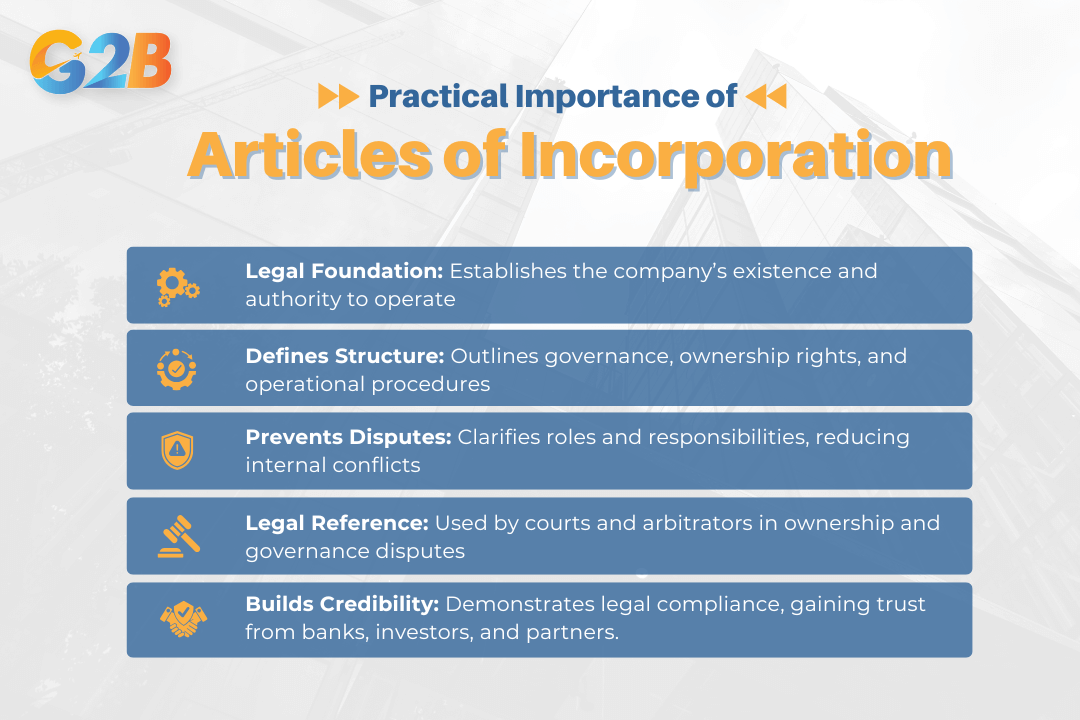
The Articles of Incorporation serve as the fundamental legal document that establishes a company’s existence, providing the basis for its management and operations. This document creates the legal framework within which all business activities must occur, establishing the company's authority to conduct business and defining the scope of its operations. These articles help prevent internal disputes by clearly defining the rights and responsibilities of all relevant parties. By establishing clear governance structures, ownership rights, and operational procedures, the articles reduce ambiguity and provide a reference point for resolving conflicts that may arise during business operations.
They also serve as a legal reference in disputes related to ownership, governance, and the operation of the company. Courts, arbitrators, and other legal authorities rely on the Articles of Incorporation to understand the company's structure and the intentions of its founders when resolving business disputes. Furthermore, these documents are essential for establishing credibility with banks, investors, suppliers, and customers. They demonstrate that the business is properly formed and legally compliant, which is crucial for building trust and securing business relationships.
Articles of Incorporation have practical importance in business
Articles of Incorporation in Vietnam
Different from the U.S., in Vietnam, Articles of Incorporation are not explicitly mentioned as a single, separate document like in some other jurisdictions. Instead, the equivalent concept is captured within the company charter (or articles of association) and the Investment Registration Certificate (IRC) and Enterprise Registration Certificate (ERC). These documents collectively define the company's structure, operations, and legal standing.
Vietnamese companies must comply with the Law on Enterprises, which requires specific documentation during the business registration process. For foreign investors who want to register a company in Vietnam, professional service providers can assist with preparing the company charter, obtaining the necessary certificates, and ensuring full legal compliance. The company charter serves a similar function to Articles of Incorporation, outlining the company's objectives, capital structure, management organization, and operational procedures. Foreign investors establishing businesses in Vietnam must also obtain appropriate certificates depending on their business activities and investment scale.
Understanding these local requirements is crucial for Vietnamese businesses expanding internationally or foreign companies entering the Vietnamese market. The principles underlying Articles of Incorporation remain relevant even when the specific documentation requirements differ, as they represent fundamental concepts of corporate governance and legal structure that apply across different jurisdictions.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
