In today's complex business environment, establishing and operating a company requires strict adherence to legal regulations and corporate governance principles. Among the most critical documents that every company must possess are the Articles of Association. These documents serve not merely as mandatory legal requirements but as the internal constitution that governs all aspects of corporate operations and stakeholder relationships.
What are articles of association?
Articles of Association are internal documents that outline the rules and regulations for managing and operating a company. They serve as an internal legal code and a contract between the company and its shareholders, defining the rights and responsibilities of all relevant parties. The Articles represent a crucial part of the company's governing documents and are a mandatory legal requirement under corporate law.
These documents establish the fundamental framework for how a company conducts its business, makes decisions, and manages relationships between various stakeholders. They provide the legal framework for managing the company's internal affairs and ensure that all parties understand their roles, rights, and obligations within the corporate structure.
Main contents of the articles of association
The Articles of Association contain several essential components that collectively define the company's operational framework and governance structure. Each element serves a specific purpose in establishing clear guidelines for corporate management and stakeholder relationships.
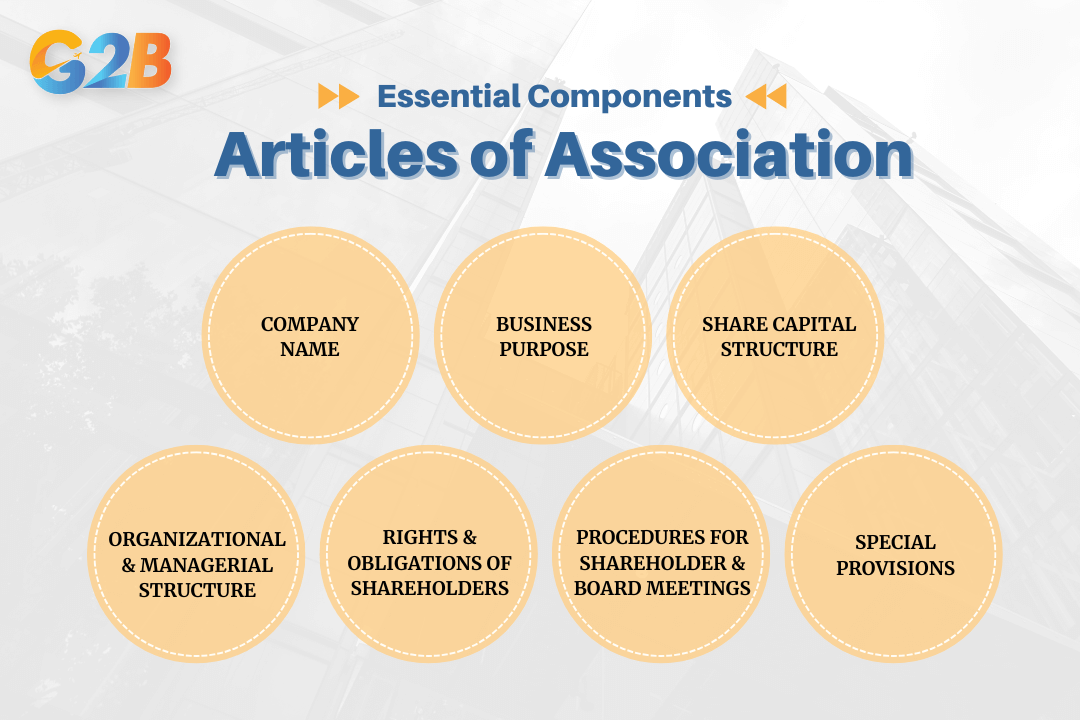
The Articles of Association contain several essential components
- Company name: As a legal entity, a company must be assigned a formal name, as stated in its Articles of Association. This name generally includes an ending like “Inc.” or “Ltd.” to signify its corporate nature.
- Business purpose: Specifies the scope of business activities and defines the company's authorised operations and objectives.
- Share capital structure: Types and number of shares, share transfer rights, and mechanisms related to equity distribution, including dividend entitlements.
- Organizational and managerial structure: Number, powers, and responsibilities of directors, appointment process, board meetings, and management hierarchy.
- Rights and obligations of shareholders: Voting rights, participation in general meetings, and any special rights or privileges accorded to different shareholder classes.
- Procedures for shareholder and board meetings: Notifications, quorum requirements, voting methods, and resolutions required for various corporate decisions.
- Special provisions: Special provisions such as confidentiality clauses, pre-emptive rights, drag-along clauses, and share valuation mechanisms in transfers and other corporate transactions.
Articles of association vs memorandum of association
While both documents are essential for company formation, they serve distinct purposes in corporate governance and legal compliance.
Fundamental differences
The Memorandum of Association defines the company's founding purpose, scope of activities, and relationship with the external world. It establishes the company's legal identity and defines what the company can do. In contrast, the Articles of Association detail the internal management structure, specifying how the company will operate internally and how decisions will be made.
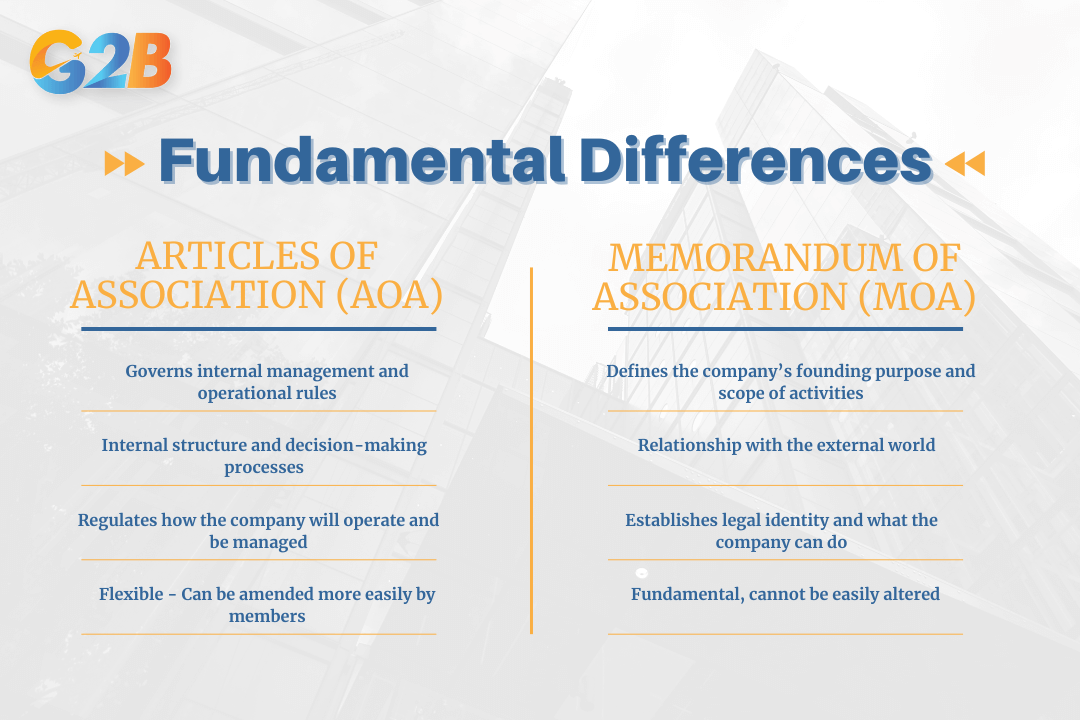
Articles of association vs memorandum of association have distinct purposes in corporate governance
Complementary roles
These documents work together to provide a complete legal framework for corporate operations. The Memorandum establishes the company's external boundaries and legal capacity, while the Articles govern internal processes, management structures, and stakeholder relationships. Together, they create a comprehensive governance system that ensures legal compliance while enabling efficient business operations.
Legal validity and binding nature
The Articles of Association carry significant legal weight and create binding obligations for all parties involved in the company's operations. The Articles are a legally binding document, enforceable on the company, its shareholders, and directors, creating contractual obligations and legal rights. They can be amended or supplemented through a special resolution at a shareholders' meeting, ensuring democratic decision-making in corporate governance changes. Must be filed with the company registry and are publicly accessible, promoting transparency and enabling stakeholders to understand corporate structures.
Practical importance and applications of articles of association
The Articles of Association serve multiple practical purposes that extend far beyond mere legal compliance, providing tangible benefits for corporate operations and stakeholder relationships. Serves as an "operating manual" for corporate governance, promoting transparency and efficiency in decision-making processes and daily operations. Protects shareholder rights and helps prevent internal disputes by establishing clear procedures for conflict resolution and stakeholder communication. Aids in legal compliance and builds investor and partner confidence by demonstrating professional corporate governance and regulatory adherence.
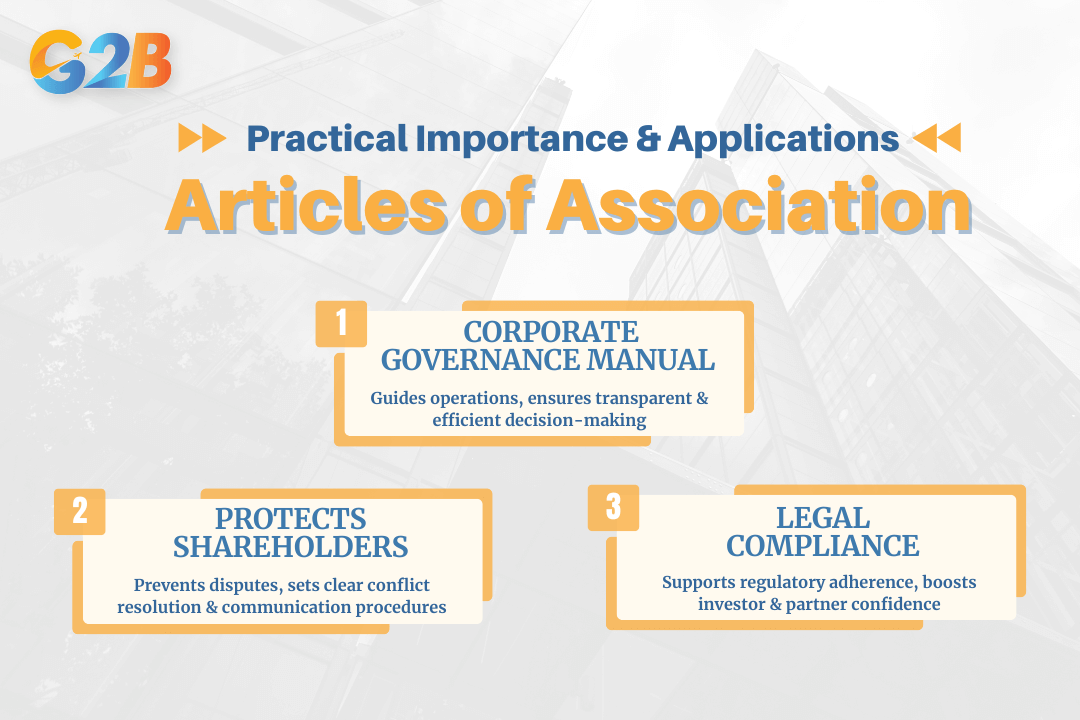
Practical importance and applications of articles of association
Important notes on Articles of Association in Vietnam
The Articles of Association (AoA) have certain requirements unique to Vietnam that companies and investors need to understand. Below are key points specific to the Vietnamese market, particularly important for foreign entrepreneurs who want to start company formation in Vietnam.
- Legal term in Vietnam: In Vietnam, the AoA is referred to as the Company Charter, which serves as the primary legal document governing a company’s structure and operations.
- Mandatory for company registration: The Company Charter is a compulsory document when conducting business registration in Vietnam, applicable to all legal entity types, including LLCs and JSCs.
- Language and format: The document must be prepared in Vietnamese. If a bilingual version (Vietnamese - English) is used, the Vietnamese version prevails in case of any discrepancies or disputes.
- Minimum content requirements under the Law on Enterprises: It must include: company name, registered office, business activities, charter capital, list of members/shareholders, their rights and obligations, management structure, voting procedures, profit distribution, loss handling, dispute resolution mechanisms, remuneration for management, conditions for capital contribution withdrawal, and dissolution procedures as required under Vietnamese law.
- Capital contribution and liability: The AoA should specify capital contribution commitments and the liability of members/shareholders if they fail to contribute capital as agreed - a key concern for foreign investors.
- Amendments and updates: Any major changes, such as capital increases, changes in members/shareholders, or management structure, must be reflected in the AoA and registered with the competent authority.
- Legal binding effect: The AoA is legally binding on the company and its members/shareholders. Breaches can lead to internal disputes or legal liabilities.
FAQs about articles of association
Understanding the Articles of Association (AoA) is crucial for anyone looking to establish or manage a company in Vietnam, as it defines the fundamental rules governing corporate structure and operations. Below are some frequently asked questions that clarify key aspects of the AoA.
1. Who has the authority to create the Articles of Association?
The Articles of Association are created by the founding members or shareholders of the company, through the drafting and signing of the document during the business incorporation process.
2. How are the specific rights and obligations of shareholders defined in the Articles of Association?
The rights and obligations of shareholders in the Articles of Association typically include the right to attend and vote at general meetings, receive dividends, have pre-emptive rights to purchase new shares, and freely transfer shares within legal boundaries. Shareholders are also obliged to fully pay for the shares they have subscribed to and comply with the company’s regulations.
3. How can internal disputes be resolved through provisions in the Articles of Association?
The Articles of Association often outline mechanisms for resolving internal disputes through negotiation, mediation, commercial arbitration, or court proceedings. They may also include procedures for special meetings and voting to ensure that disputes are handled transparently and effectively.
4. What are "entrenchment" provisions in the Articles of Association, and how do they affect amendments to the document?
Entrenchment provisions are clauses that protect certain important sections of the Articles from being easily amended. These provisions usually require a higher voting threshold or special consensus to make changes, thereby preserving stability in corporate governance.
5. Who has the authority to enforce and litigate violations of the Articles of Association within the company?
Shareholders, the company itself, and regulatory authorities all have the right to enforce and initiate legal proceedings in the event of violations of the Articles of Association, in order to protect legal rights and ensure compliance with the company’s constitution.
6. How are the mechanisms for appointing, removing, and retiring directors defined in the Articles of Association?
The Articles of Association clearly set out the powers related to the appointment, removal, term of office, and retirement policies of directors, ensuring transparent, accountable, and effective company management.
The Articles of Association represent an essential foundational document for corporate governance, clearly defining the roles, powers, and responsibilities of all parties involved in company operations. They ensure that a company operates transparently, effectively, and lawfully while protecting the interests of shareholders, directors, and other stakeholders.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
