A Private Limited Company (Ltd.) stands as one of the most powerful and trusted business entities worldwide, with over 95% of companies registered in the UK as private limited companies. From attracting investors to ensuring long-term stability, this model provides businesses with the legal framework to scale, innovate, and thrive. Whether you are launching a startup or expanding your enterprise, understanding the strategic benefits of a Private Limited Company is essential.
Understanding a Private Limited Company
Discover the intricate details that can set your venture on the path to success.
What is a Private Limited Company?
A Private Limited Company is a corporate structure that combines the advantages of both partnership and corporation. This entity is recognized for its distinct legal identity, meaning it can own property, incur liabilities, and enter into contracts independent of its shareholders. It acts as a separate entity, which offers owners the benefit of limited liability protection. In essence, the shareholders' personal assets remain protected in cases of business insolvency or lawsuits, with their financial responsibility limited to their investment in shares.
If you are interested in Parnership and Corporation, you can read more about Partnership vs Corporation
Legal characteristics and status
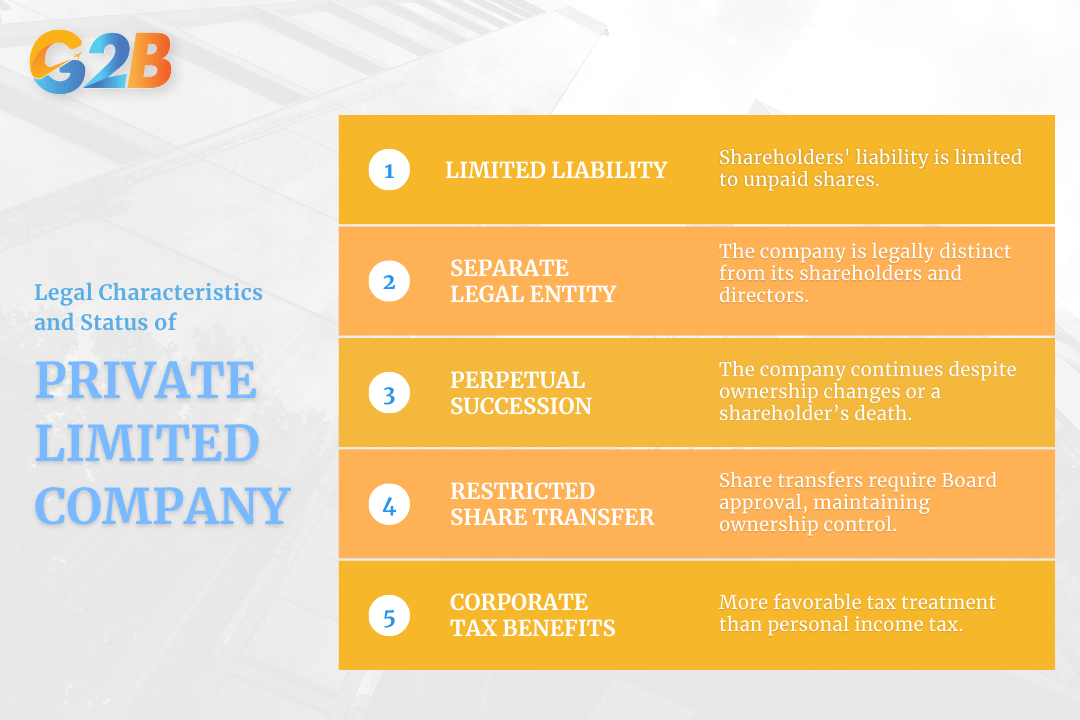
The legal characteristics of a Private Limited Company solidify its status as one of the most preferred business entities worldwide. Here are several key features:
- Limited liability: Shareholders are only liable for the company's debts up to the amount unpaid on their shares.
- Separate legal entity: The company is perceived as a legal "person" in the eyes of the law, separate from its shareholders and directors.
- Perpetual succession: The company’s existence is not affected by changes in ownership or the death of a shareholder. This continuity is vital for maintaining partnerships and investor confidence.
- Restrictions on transferability of shares: Generally, shares in a Private Limited Company cannot be transferred freely and require the pre-approval of the Board of Directors. This restriction ensures control over who becomes part of the ownership.
- Corporate tax benefits: This structure commonly has more favorable tax treatment compared to personal income tax.
Explore the legal characteristics and status of a Private Limited Company
Structure and shareholder roles
The relationships between these roles below are critical, as they ensure the company functions smoothly and complies with legal standards. Understanding the structure of a Private Limited Company is crucial for grasping how it operates:
- Shareholders: The owners of the company who hold shares representing a portion of the company's equity. They have the right to vote on major decisions and receive dividends.
- Directors: Appointed by the shareholders to manage the company’s affairs. Directors are responsible for strategic decision-making and ensuring legal compliance.
- Board of directors: This is a governing body composed of elected representatives charged with protecting shareholders' interests and overseeing management. Meetings are held regularly to discuss the company's strategy and operations.
- Company secretary: Although optional in some jurisdictions, a company secretary is responsible for governance-related matters, ensuring regulatory compliance, doing the paperwork, and maintaining statutory registers and records.
Registration process and legal requirements
A Private Limited Company offers a robust structure with considerable benefits, such as limited liability, corporate tax efficiencies, and perpetual succession. To form a Private Limited Company, specific legal steps and documentation are required. This usually involves:
- Memorandum of association: A document that outlines the company’s purpose and its relationship with the external environment.
- Articles of association: This includes the company's internal management rules and regulations.
- Incorporation documents: Submitted to a country's relevant authority, such as Companies House in the UK or the Ministry of Corporate Affairs in India. This process grants the company legal recognition.
Legal framework and incorporation process
Let’s delve into the essential components required for incorporation and clarify the roles of some business regulatory authorities in various countries, such as Companies House and the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, key bodies pivotal in the process.
Key legal documents needed
Forming a private limited company necessitates the preparation of certain critical legal documents. Firstly, the Memorandum of Association outlines the company’s structure and purpose. It serves as a declaration by initial shareholders marking their intention to form a corporation. The Articles of Association act as the governing document, detailing regulations for the company's operations and defining the responsibilities of its directors and shareholders. Another requisite document is the statement of capital, which outlines the company’s share structure, including the number of shares and their value.
Steps to incorporate a Private Limited Company
Incorporating a private limited company is a structured process involving several key steps. Each country has its own regulatory body. For example:
- UK: Companies House manages company registrations.
- India: The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) is exclusively responsible for regulating companies incorporated and operating in India.
- USA: Business regulations are handled at the state level (e.g., Delaware Division of Corporations).
- Singapore: ACRA (Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority) oversees businesses.
The structured approach ensures that all legal prerequisites are met, providing the company with a solid regulatory foundation upon which to operate:
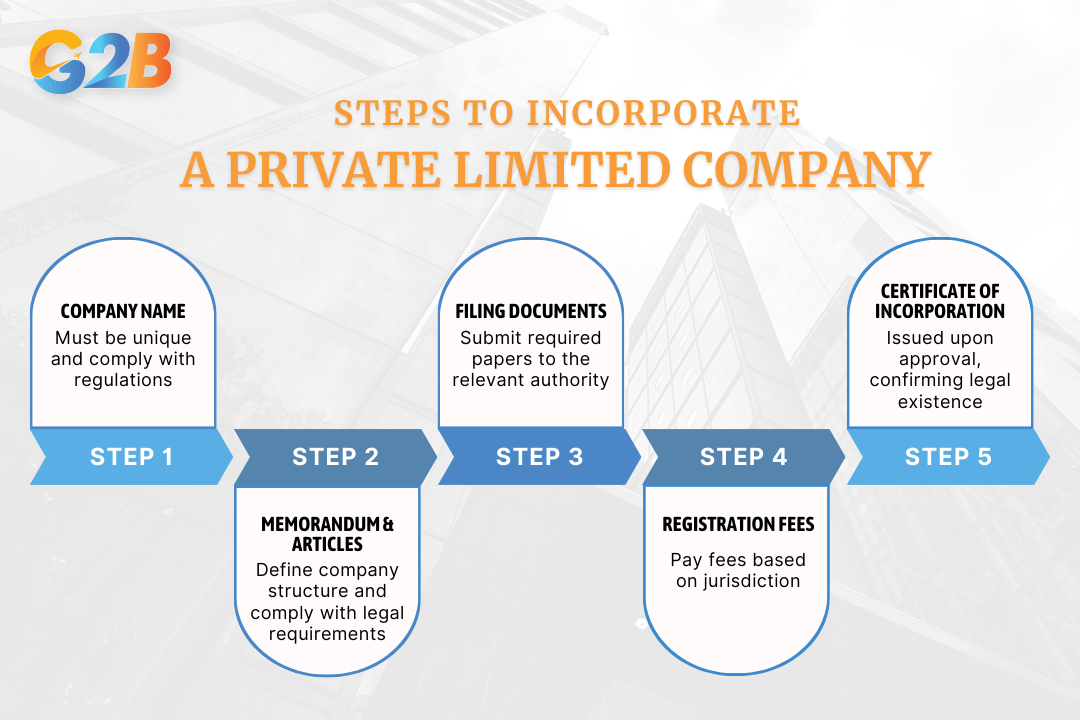
- Choosing a company name: The name must be unique and comply with local regulations, avoiding existing trademarks and prohibited terms.
- Drafting the memorandum and articles of association: Tailored to the company's needs, these documents must comply with legal requirements and reflect the internal protocol.
- Filing with the Companies House or the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (India): Submission of all necessary documents, including the memorandum, articles, and details of the directors and subscribers, is essential.
- Payment of registration fees: Incorporation involves a fee, which varies by jurisdiction and must be paid during the submission.
- Issuance of the certificate of incorporation: After verification, authorities issue this certificate, officially recognizing the company as a separate legal entity.
Explore 5 steps to incorporate a Private Limited Company
Role of the companies house and the ministry of corporate affairs
The Companies House in the UK and the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) in India are crucial in the incorporation process. Together, these bodies ensure the smooth and lawful operation of private limited companies, promoting growth, trust, and integrity across the business landscape. Each of these bodies serves a unique set of functions:
- Companies House (UK): Tasked with maintaining the official register of companies, its responsibilities include verifying submitted documents, facilitating the disclosure of corporate information, and ensuring compliance with Companies Act regulations. It plays a vital role in promoting transparency and supporting investors and stakeholders in their decision-making processes.
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (India): Equivalent to the Companies House, the MCA oversees company registration, monitors corporate governance practices, and enforces statutory compliance under the Companies Act 2013. The MCA also updates regulations to adapt to economic changes and promotes a business-friendly environment.
Advantages of a Private Limited Company
A private limited company (Pvt. Ltd.) is a popular business structure for entrepreneurs and small business owners due to its unique benefits. Understanding these benefits helps individuals choose the most fitting legal structure for their business ventures.
Investigate the 3 most important advantages of a Private Limited Company
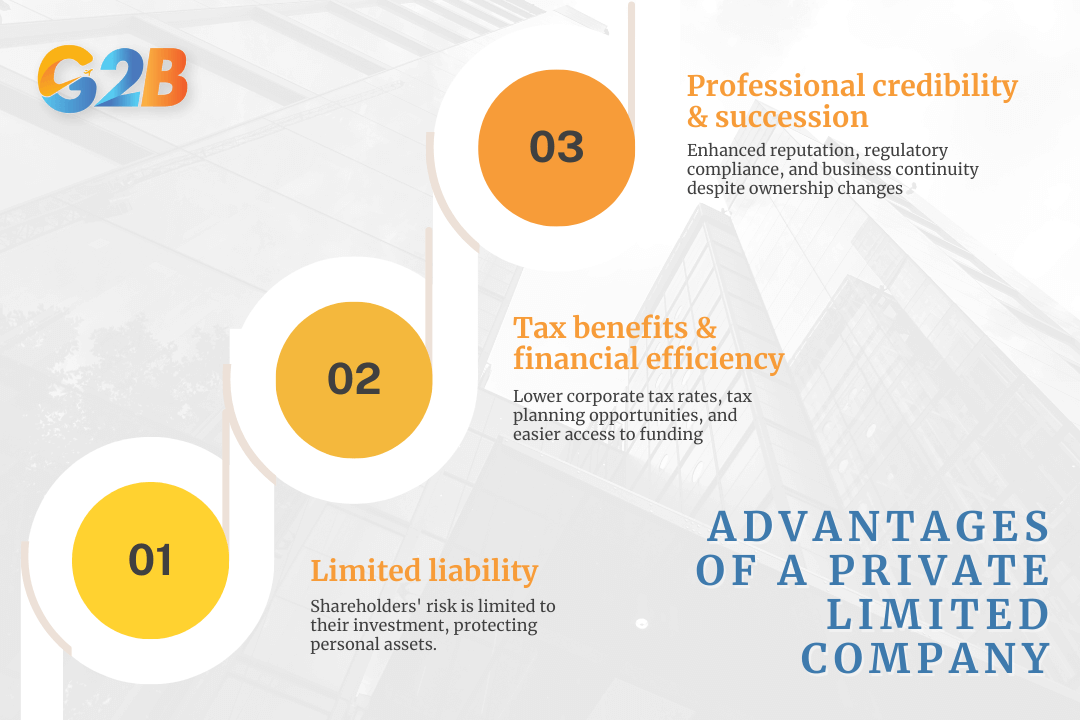
Limited liability protection
One of the most significant advantages of a private limited company is limited liability protection. Shareholders in a Pvt. Ltd. are only liable for the company's debts up to the amount they have invested. This is an essential safeguard for entrepreneurs, as it protects personal assets from being used to settle business liabilities. Essentially, if a private limited company faces financial difficulties or legal actions, shareholders' risk is limited to the unpaid value of their shares. This feature distinguishes private limited companies from sole proprietorships or partnerships, creating a layer of security for business owners.
Tax benefits and financial efficiencies
Private limited companies often have various tax benefits and financial efficiencies. In many jurisdictions, companies are subject to lower corporate tax rates compared to personal income tax rates. For instance, the UK offers corporate tax rates that are generally more favorable than individual taxation, providing significant savings for businesses operating as a private limited company. Additionally, Private limited companies have access to various tax planning opportunities, such as claiming allowable expenses that reduce taxable income.
This structure also facilitates the implementation of effective financial strategies, such as profit reinvestment and dividend distribution among shareholders, which can further optimize tax efficiencies. Furthermore, a Pvt. Ltd. can more easily access external funding from banks and investors, as entrepreneurs often view them as more stable and reliable due to their separate legal identity and structured corporate governance. This enhanced financial credibility translates into better opportunities for growth and expansion.
Professional credibility and perpetual succession
A private limited company has enhanced professional credibility compared to other forms of business ownership. The formal structure and regulatory compliance associated with a Pvt. Ltd. often signal stability and professionalism to clients, partners, and investors. The separation of ownership and management, combined with transparent reporting requirements, boosts a company's image, positioning it favorably within its industry. Moreover, Pvt. Ltd. companies benefit from perpetual succession - a feature ensuring the company's existence is not tied to the lives of its shareholders. Ownership can easily be transferred or sold, ensuring business continuity despite any changes in management or shareholder composition.
Disadvantages and challenges of a Private Limited Company
Establishing a private limited company, while offering several benefits, is not without its share of disadvantages and challenges. Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Explore some of the biggest disadvantages of a Private Limited Company
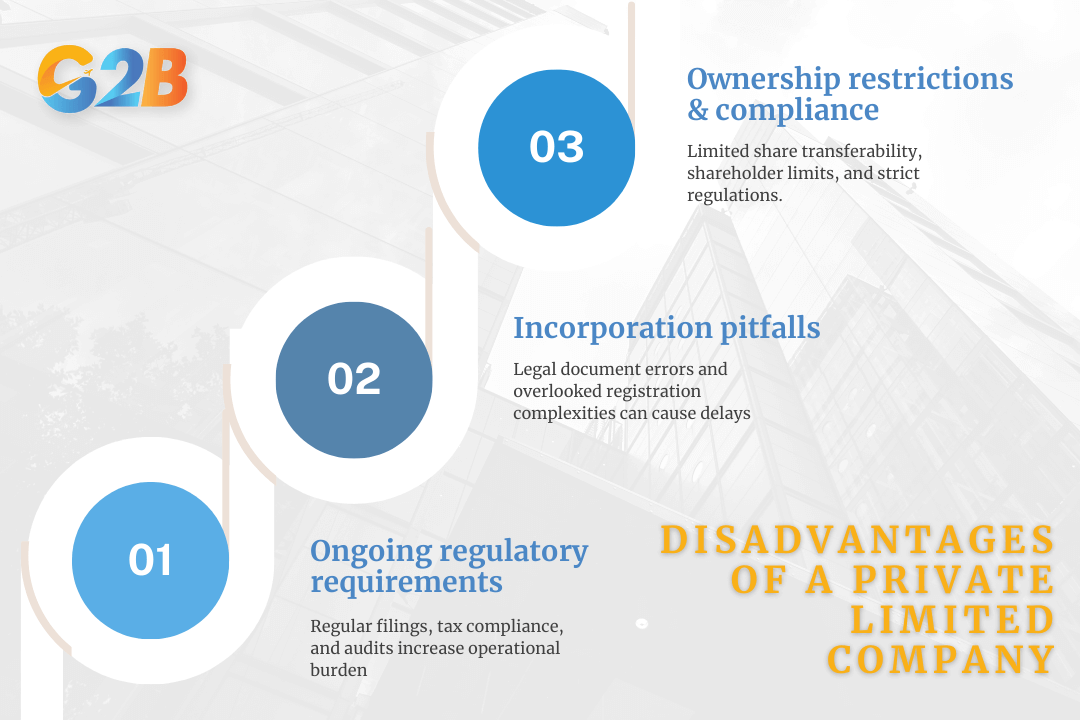
Ownership restrictions and compliance issues
One of the primary challenges faced by private limited companies is ownership restrictions. Unlike a public limited company, a private limited company restricts the transferability of shares, making it less flexible in terms of ownership changes. Furthermore, the law limits the number of shareholders, which can impede the company's ability to raise capital from a broad base of investors. Additionally, private limited companies are subject to stringent regulatory requirements, which necessitate meticulous record-keeping and regular filings with entities. Non-compliance can lead to penalties and legal repercussions.
Common pitfalls during incorporation
One common mistake is the inadequate preparation of requisite legal documents. Any discrepancies or omissions could lead to legal challenges or delays in incorporation. Another frequent challenge is underestimating the complexities involved in company registration processes. Entrepreneurs might overlook essential steps or fail to adhere to specific legal requirements, which can prolong the registration process. Engaging experienced legal advisors can mitigate these risks by ensuring that all documentation is correctly filed and that the incorporation process adheres to current legal standards.
Ongoing regulatory requirements
After successful incorporation, a private limited company must continually navigate ongoing regulatory requirements. These include regular tax filings, annual returns submissions, and compliance with employee-related laws. For instance, companies are often mandated to conduct annual general meetings and maintain updated financial records, which must be audited annually. Failure to meet these ongoing obligations can result in penalties or even legal action against the company. This ongoing regulatory burden can be an operational challenge, necessitating dedicated resources and potentially increasing overhead costs.
Comparative analysis with other business structures
The upcoming section will provide a comparative analysis to help you understand the unique advantages and limitations of this entity. Let’s discover how it compares to options like sole proprietorships, partnerships, and public companies.
Private Limited Company vs. Public Limited Company
While both private limited companies and public limited companies offer limited liability protection and exist as separate legal entities, they cater to different needs:
- Accessibility of capital: PLCs are designed to raise capital from the public through the stock exchange, allowing for potentially vast resources. In contrast, Pvt. Ltd. companies secure funding from private investors, making it a more controlled environment.
- Regulatory compliance: PLCs must comply with stringent disclosure norms and regulatory requirements due to their public nature. This ensures transparency for shareholders but can be costly and time-consuming. Pvt. Ltd. companies face fewer regulatory burdens, reducing overhead and administrative costs.
- Ownership structure: Shares of a PLC are freely transferable, promoting liquidity but also increasing the potential for a hostile takeover. In contrast, Pvt. Ltd. companies restrict share transfers, ensuring ownership remains within a trusted circle, such as close family or business associates.
Comparison with Limited Liability Companies
Although both private limited companies and LLCs provide limited liability for their members, several distinctions exist based on jurisdictional specifics:
- Flexibility in management: LLCs often offer more flexible management structures, not requiring a board of directors or annual meetings. This can be advantageous for smaller businesses that prioritize operational nimbleness. Pvt. Ltd.'s necessitate more formal organizational structures, which can enhance professional credibility.
- Taxation: LLCs benefit from pass-through taxation in jurisdictions like the United States, wherein income is directly passed to owners to be taxed as personal income, avoiding corporate tax. Pvt. Ltd. companies often benefit from fixed corporate tax rates, which can be lower than personal tax rates in some regions.
- Legal status and formation: Establishing an LLC can be quicker and often involves less paperwork than setting up a Pvt. Ltd.. However, Pvt. Ltd. structures may offer superior credibility, especially in international business scenarios or with more conservative institutions.
Pros and cons of Partnership models
Partnerships, whether general or limited, represent another essential business structure but differ significantly from Pvt. Ltd. companies:
- Liability: General partners in a partnership are directly liable for business debts, unlike the limited liability protection offered by Pvt. Ltd. companies. This heightened personal risk can be a key deterrent.
- Resource sharing and decision making: Partnerships bring diverse expertise and resource pooling, but can suffer from conflicts and disagreements without formal conferred roles. Pvt. Ltd. companies with defined shareholder roles tend to offer clearer decision-making hierarchies.
- Profit distribution and taxation: Partnerships enable flexible profit-sharing arrangements and can sometimes provide advantageous tax treatments through direct income distribution. Pvt. Ltd. companies distribute profits as dividends, which may be subject to additional taxes.
Private limited companies offer a balanced mix of liability protection, regulatory control, and professional credibility, making them a favorable choice for many businesses. However, understanding the nuances of each business structure - PLCs, LLCs, and partnerships - is crucial to align with the specific business objectives and requirements.
Step-by-step guide to company formation
Understanding the process in detail ensures not only legal compliance but also sets the stage for operational success. There are 3 primary segments: initial planning and research, completing the registration process, and opening a business bank account.
Initial planning and research
Before embarking on the legalities of company formation, it's imperative to engage in thorough planning and research. This phase sets your business on the right path and involves several critical considerations:
- Define your business objectives and vision: Clearly outline the purpose of your business, its goals, and the value it intends to offer. A well-defined mission can guide everything from branding to market positioning.
- Conduct market research: Understanding your target market, competitors, and industry trends is crucial. This aids in identifying your unique selling proposition and potential market gaps.
- Choose a unique company name: Select a company name that reflects your brand and complies with legal criteria. It should be unique, non-offensive, and not identical to existing registered companies. A name check with the relevant company registry, such as Companies House in the UK or the Ministry of Corporate Affairs in India, is necessary to prevent conflicts.
- Identify suitable business structure: While a private limited company might be ideal for limited liability and scalability, assess if it's the best fit against alternatives like LLCs or sole proprietorships, depending on your business needs.
- Secure initial funding: Consider how you will finance your company. Whether through personal funds, loans, or investment, ensure that you have a clear financial plan.
Completing the registration process
The registration of a private limited company involves adherence to specific legal procedures. By following these steps meticulously, you ensure regulatory compliance and the legal standing of your business:
- Prepare required documentation: Accumulate all necessary documents, including the Memorandum and Articles of Association, which outline your company’s constitution and rules governing it.
- Appoint directors and shareholders: As legally required, appoint at least the minimum number of directors and shareholders. Ensure that all parties involved understand their roles and responsibilities.
- Register with the appropriate authorities: File your application with the relevant authorities, such as Companies House in the UK. Provide all requisite information such as company name, registered office address, and director details.
- Pay the registration fee: There is typically a fee associated with company registration. This fee varies by jurisdiction and can often be paid online.
- Receive certification of incorporation: Upon approval of your application, you will receive a Certificate of Incorporation. This document confirms your company’s legal existence.
Opening a business bank account and accounting setup
Post-registration, ensuring a strong financial management system is key. This includes opening a business bank account and establishing accounting protocols:
- Set up a business bank account: Choose a bank that offers facilities tailored for businesses. Ensure that the account provides functionality for transactions, online banking, and potentially international dealings if required.
- Implement an accounting system: Establish an accounting system that can handle payroll, tax filings, and financial reporting. This may involve hiring an accountant or investing in accounting software.
- Register for taxes: Ensure you are registered for relevant taxes like VAT or GST, depending on your jurisdiction’s regulations. Maintaining tax compliance helps avoid legal issues.
- Establish financial controls: Implement systems for managing cash flow, budgeting, and financial forecasting. Consider conducting regular audits to ensure financial integrity.
By following these steps, you lay a strong foundation for your private limited company, ensuring compliance with legal standards and setting up the framework for effective operational management. Each step requires careful consideration and execution to foster a thriving business environment.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Let’s break down some of the most asked questions to give you clear, concise answers about a private limited company’s benefits, legal requirements, and operational structure.
Can a single person form a Private Limited Company?
Yes, a single individual can form a private limited company, a concept commonly referred to as a One Person Company (OPC) in several jurisdictions. The process involves distinct legal frameworks depending on the country, but generally shares some common steps:
- Legal framework and eligibility: In some countries, such as India, the Companies Act allows for the creation of an OPC. This simplifies the formation process for entrepreneurs who want to experience the benefits of limited liability while maintaining full control over their business operations.
- Benefits of forming an OPC: Single individuals forming a private limited company benefit from limited liability protection, where their personal assets are separate from company liabilities. This structure also allows a sole proprietor to enjoy a separate legal entity status, potentially attracting investment and providing a more formal business image.
- Incorporation process: The incorporation process generally requires the submission of a Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association, alongside identification and address proof of the sole director/shareholder, to the regulatory body responsible for company registrations, such as Companies House in the UK or the Ministry of Corporate Affairs in India.
What are the tax liabilities of directors?
Directors of a private limited company have specific tax liabilities that require careful management:
- Personal income tax: Directors typically draw salaries which are subject to personal income tax according to the prevailing tax brackets in their country of residence. This requires ensuring the correct withholding and timely payment of taxes.
- Dividend taxation: Directors who are also shareholders might receive dividends, which could attract additional tax. Depending on the local tax laws, dividends could be taxed at a different rate, often lower than regular income tax, encouraging profit distribution through dividends.
- Corporate tax obligations: Although directors are not directly liable for corporate taxes, they are responsible for ensuring compliance with corporate tax regulations. This includes filing timely returns and aligning company financial practices to optimize tax efficiency, using advice from legal advisors and accountants.
- Fringe benefits and other allowances: Certain benefits provided to directors, like company cars or housing, may incur tax liabilities classified as fringe benefits. Directors must accurately report and manage these elements to ensure tax compliance.
How to choose the right legal structure for a startup?
Choosing the right legal structure is critical for startup success, affecting the company's compliance obligations, tax efficiency, and ability to raise capital. Here's a concise guide to make the right choice:
- Assess business goals and growth plans: Start by understanding the business's goals. If rapid scalability and external funding are priorities, a private limited company may be more appropriate than a partnership or sole proprietorship, offering easier access to investors and limited liability protection.
- Evaluate tax implications: Different structures have varied tax obligations. For instance, sole proprietorships might face less compliance work but could see higher personal tax rates, whereas limited companies enjoy lower corporate tax rates but require intricate tax filings.
- Consider administrative complexity and compliance: Private limited companies require adherence to stricter regulatory requirements and comprehensive bookkeeping, which should be taken into account. On the other hand, simpler structures may be easier to manage administratively.
- Liability considerations: Decide based on how much personal liability you're willing to bear. Structures like a private limited company offer robust liability protection, a crucial factor for many startups looking to mitigate risk.
- Legal and market requirements: Certain industries may have statutory requirements demanding specific structures for operation. Conduct market research to ensure compliance with industry-specific regulations or licensing that may influence the chosen structure.
Choosing the right legal structure sets the foundation for a startup's operational efficiency and long-term success, balancing liability, tax efficiency, and compliance against growth ambitions and resource availability. By integrating compliance upkeep, strategic growth initiatives, and expert guidance into your operational paradigm, your private limited company can navigate the complexities of business landscapes effectively.
The United Kingdom provides a business-friendly environment for foreign investors, offering policies that support new ventures and international expansion. If you are looking for a trusted partner to help you expand your business to the UK, G2B’s UK offshore company formation service provides an efficient solution. As a leading provider of professional business support services, we specialize in helping entrepreneurs establish their presence in the UK. Connect with G2B today and unlock new global opportunities!

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
