For entrepreneurs aiming for expansion and investors seeking a secure, transparent business model, understanding the operations of a Public Limited Company (PLC) is essential. As a key driver of economic growth, the PLC structure provides unmatched access to capital, enhanced credibility, and strategic scalability. With the support of professional business support services, companies can navigate the transition seamlessly while ensuring full compliance. This exploration highlights the advantages and essential considerations that make PLCs a cornerstone of modern business success.
What is a Public Limited Company
A public limited company (PLC) is a business entity that offers its shares to the public through a stock exchange*. This accessibility to capital markets provides a company with the ability to raise significant funds by selling shares, enabling expansion and growth.
Overview of a Public Limited Company
One of the primary distinctions of a PLC is its capacity to publicly trade shares, which introduces a higher level of scrutiny and regulation. Additionally, PLCs are obliged to adhere to strict regulatory disclosure requirements. Being publicly listed requires comprehensive and periodic financial reporting, often on a quarterly and annual basis, detailing the financial health and strategic direction of the company. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and other regulatory bodies oversee these requirements to maintain market integrity and protect investor interests.
Characteristics and legal framework
The legal framework surrounding public limited companies is stringent. These entities must comply with numerous legal obligations that govern their formation, operation, and reporting duties. Fundamental characteristics of a PLC include:
- Shareholder structure: PLCs often have a diverse base of shareholders, including institutional investors such as pension funds and mutual funds, alongside individual investors. This diversity requires robust mechanisms for shareholder engagement and communication.
- Corporate governance: A PLC must implement stringent corporate governance practices. This involves constituting a board of directors responsible for overseeing the company's management and ensuring that the company's strategy aligns with shareholder interests.
- Regulatory compliance: PLCs are subject to regulatory compliance under laws such as the Companies Act 2006 in the UK or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 in the US. These laws mandate regular audits and financial disclosures, which aim to maintain transparency and prevent malpractices.
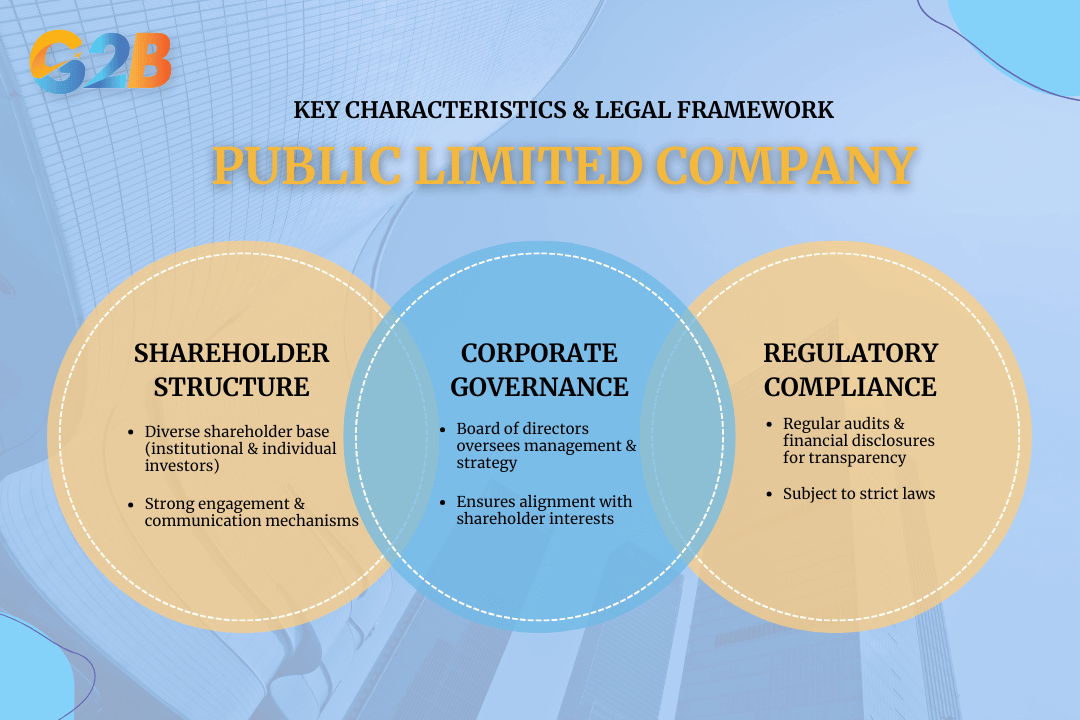
The fundamental characteristics of a PLC include 3 features
Comparison with Private Limited Company
In contrast to private limited companies, PLCs have several distinctive features. While private companies also offer limited liability protection, they are privately held and usually restrict share transfer among a limited number of shareholders. Here are the key differences:
| Feature | Public Limited Company | Private Limited Company |
|---|---|---|
| Share trading | Publicly traded on a stock exchange | Shares not offered to the public |
| Regulatory requirements | Subject to extensive regulatory scrutiny and transparency obligations | Limited regulatory oversight |
| Capital raising | Can raise capital through public markets | Limited to private funding from known investors |
| Shareholder base | Widely held with potential institutional investment | Typically smaller, close-knit group |
Understanding these distinctions helps stakeholders and potential investors make informed decisions about engagement with either type of company structure. For businesses contemplating transitioning from a private to a public limited company, this transition can bring increased capital access, but also elevates the level of public accountability and pressure from shareholders.
Exploring the IPO process for PLC
The process of taking a private company public through an Initial Public Offering (IPO) is a significant milestone for any business. It transforms the company's financial and operational landscape by opening up ownership to public investors (However, a company can become a PLC without an IPO).
Understanding initial public offerings
An IPO represents the first time a company offers its shares to the public, transitioning from a privately held entity to a public one. This process enables a company to raise substantial capital from a broad pool of investors, which can be used to fund growth initiatives, pay off debt, or expand into new markets. The journey to becoming publicly traded is multifaceted and involves numerous financial, legal, and strategic considerations.
Steps in the IPO process
The IPO process can be divided into several key phases:
- Preparation and planning: Before initiating an IPO, a company must assess its readiness for the public market. This involves evaluating the robustness of its financial health, corporate governance structures, and market position. Legal and financial advisors typically conduct this due diligence to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and to identify potential areas for improvement.
- Hiring investment banks and underwriters: Investment banks play a pivotal role in guiding a company through its IPO journey. They act as underwriters, helping to determine the initial offer price of the shares, facilitating the sale to institutional and retail investors, and often guaranteeing a certain number of shares will be sold. Selecting the right investment bank is crucial, as their expertise and market reach can significantly impact the IPO's success.
- Regulatory filings and approval: A critical component of the IPO process is complying with regulatory requirements. For example, in the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) mandates that companies file a detailed prospectus that provides comprehensive information about the company's business model, financial condition, and risks. This document must be meticulously reviewed and approved before the company can begin selling shares to the public.
- Roadshow and marketing: Once regulatory approval is secured, the company embarks on a roadshow series of presentations and meetings with potential investors to generate interest and build demand for the stock. This stage is pivotal for setting the final offer price, as feedback from these meetings influences market valuation and pricing strategies.
- Pricing and issuance: On the day before the IPO, the company, in consultation with its underwriters, sets the final offer price for the shares. This price reflects the anticipated market demand and the valuation agreed upon by both parties. The IPO concludes with shares being officially listed on a stock exchange, such as the New York Stock Exchange or NASDAQ, where public trading commences.
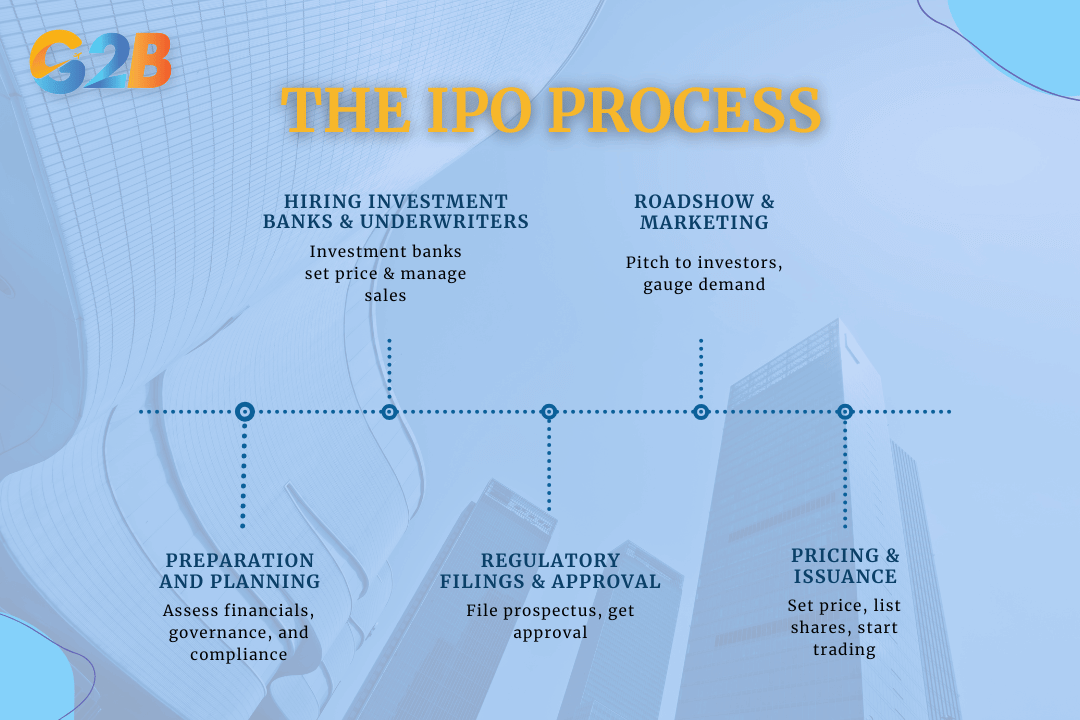
The IPO process can be divided into 5 key phases
Role of investment banks and underwriters
Investment banks and underwriters are integral to the IPO process, primarily responsible for pricing the shares and ensuring a successful entry into public markets. They manage the risk associated with the offering by underwriting, which involves purchasing all available shares from the company and reselling them to investors. This mechanism provides the company with guaranteed capital while also facilitating a smooth transition to public trading. Through meticulous preparation and collaboration with financial experts, companies can harness the IPO to fuel growth and enhance corporate stature.
Regulatory requirements and compliance
Navigating the intricate landscape of regulatory requirements and compliance is pivotal for any public limited company aiming to thrive in financial markets.
Key regulatory bodies and their roles
Public limited companies (PLCs) operate under a regulatory framework that ensures market integrity and investor protection. Key authorities, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the U.S. and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the U.K., enforce compliance with financial regulations. Other jurisdictions have equivalent bodies, like the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) and National Stock Exchanges, which set specific guidelines. These regulators collectively uphold transparency, stability, and investor confidence in capital markets.
Disclosure and transparency obligations
Disclosure forms the essence of regulatory compliance for PLCs. These entities must uphold rigorous transparency standards to maintain investor trust and market credibility. Key obligations encompass the timely dissemination of material information affecting company performance and strategic shifts.
- Prospectus disclosure: Essential for public offerings, this document provides potential investors with detailed insights into a company's financial health, risks, and governance structure. Its precision is vital, as discrepancies can result in legal repercussions and financial penalties.
- Ongoing reporting requirements: Beyond initial disclosures, PLCs are obliged to furnish periodic reports, such as quarterly and annual financial statements, ensuring sustained transparency. This continuous reporting aids in evaluating the company's trajectories and financial standing.
- Insider trading and material events: Companies must adhere to regulations governing the disclosure of insider trading activities and material events. Timely disclosure of such occurrences minimizes market manipulation and promotes fair trading practices.
Annual reports and financial audits
Annual reports and audits are integral to demonstrating financial integrity and compliance. These documents serve as formal presentations of a company's financial activities, offering stakeholders a comprehensive analysis of its fiscal performance and governance practices.
- Annual reports: These documents are comprehensive statements encompassing financial performance, corporate strategy, and governance practices. Key components include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, offering insights into financial health and operational efficacy. Additionally, the narrative sections outline strategic achievements, risk management, and future outlook.
- Financial audits: Independent financial audits are pivotal in verifying the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. Conducted by external auditors, these examinations provide an unbiased assessment of financial records, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. Audits reinforce the credibility of financial disclosures, fostering investor confidence in the company's transparency and accountability.
Benefits of going public
Going public, or offering shares to the public through a stock exchange, can be a transformative step for any business. Below are critical benefits that businesses can receive.
Access to capital markets
One of the primary motivations for a company to go public is to access broader capital markets. This access provides a means to raise substantial funds for various purposes - Whether it be expanding operations, launching new product lines, or paying off existing debts. By selling shares to the general public, companies can capitalize on the stock market’s potential to generate significant amounts of investment. Access to capital markets ensures that a company can pursue opportunities it might otherwise miss due to financial constraints.
Enhancement of corporate credibility
Public companies are seen as more transparent and well-managed due to the stringent regulatory standards they must adhere to, enforced by bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission. The necessity of regular financial reporting and adherence to corporate governance protocols builds trust with stakeholders, from investors to partners and even customers. This trust can lead to enhanced business relationships and improved terms with suppliers and creditors.
Increased visibility and public image
Increased media exposure is another significant benefit of going public, as public companies are frequently covered by financial analysts and reported in the media. Such visibility can play a crucial role in brand-building and customer awareness. As a company gains recognition, it can improve its competitive position in the market. This increased visibility offers a dual advantage: It not only attracts potential investors who might not have considered the company in its private days, but also boosts its brand's strength in the eyes of consumers.
By integrating with the public financial markets, companies also get the opportunity to use their stock as currency. This can be particularly useful in mergers and acquisitions, allowing a business to avoid large cash outflows. Additionally, the liquidity provided by a public market listing makes it easier for early investors, such as venture capitalists and angel investors, to exit their investments, providing an attractive return for their initial involvement.
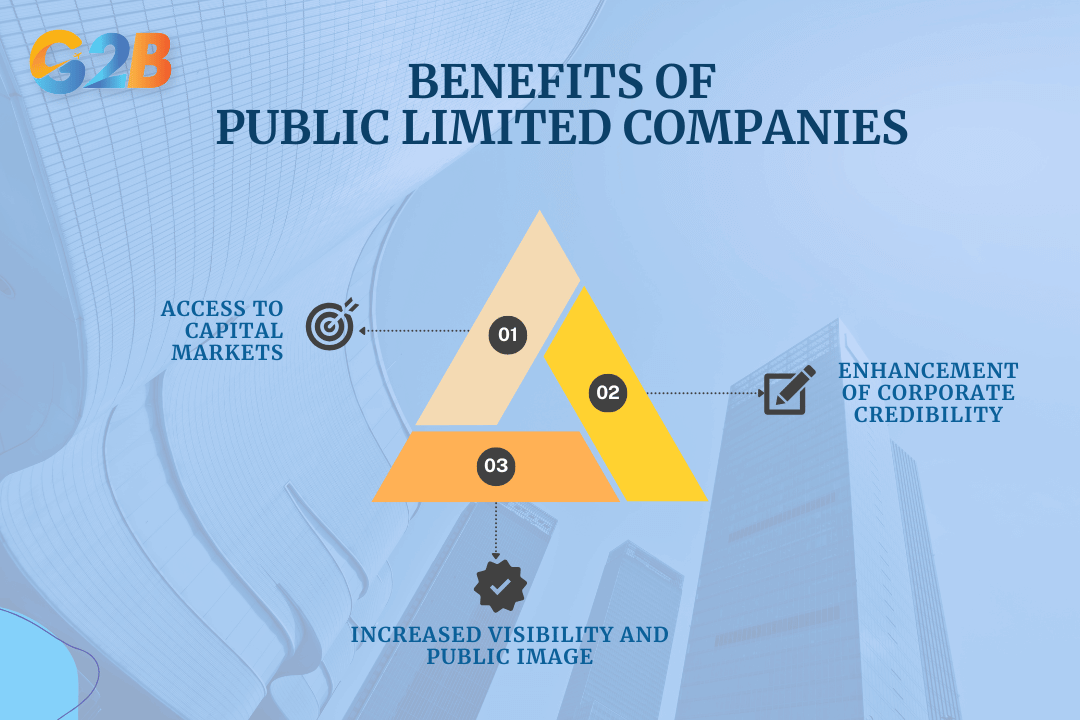
3 critical benefits of PLC structures that businesses can receive
Challenges and risks of public listing
Public listing, though offering significant benefits, also presents challenges and risks that companies must navigate carefully. Understanding these pitfalls is essential for businesses contemplating a move to the public domain.
Market volatility and price fluctuations
Public limited companies face significant market volatility, with share prices fluctuating due to economic conditions, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. This unpredictability can impact market capitalization and corporate reputation. Even financially stable companies may experience sharp declines during economic downturns. Such volatility poses challenges for long-term planning and investor confidence.
Shareholder expectations and pressure
Public companies face pressure from shareholders to maintain strong financial performance, often prioritizing short-term gains over long-term strategy. This can lead to increased scrutiny of corporate decisions and influence through voting rights. Balancing shareholder expectations with sustainable growth is a constant challenge. Failure to do so may result in strategic missteps or loss of investor confidence. Managing these demands requires careful planning and transparency.
Regulatory scrutiny and compliance costs
Public limited companies face strict regulatory scrutiny and must comply with financial disclosure and corporate governance requirements. This entails significant compliance costs, including legal and accounting expenses. Ensuring adherence demands time and resources, especially for smaller firms. Non-compliance can result in fines, legal issues, and reputational damage. Maintaining high compliance standards is essential for stability and investor trust.
Balancing internal governance and market expectations
Navigating the complexities of internal corporate governance while meeting market expectations is another significant challenge. Public companies must establish robust governance structures to ensure transparency and accountability. This involves forming effective boards of directors, implementing sound internal controls, and fostering a culture of ethical business conduct. Therefore, maintaining effective governance practices is integral to sustaining investor confidence and minimizing potential risks.
Increased public and media scrutiny
The transition to a public company brings with it increased scrutiny from both the public and media. Every corporate move, executive decision, and financial performance is closely watched and analyzed, often in real-time. Negative news or poor earnings can rapidly lead to public criticism, impacting the company's reputation and shareholder value. Balancing these elements ensures not only compliance and sustainability but also long-term success in the public market sphere.
Corporate governance and investor relations
Corporate governance is a framework of processes, practices, and rules through which companies are directed and controlled. This structure serves as the backbone of a company’s integrity and transparency in its dealings with shareholders and stakeholders.
Importance of strong governance practices
Strong corporate governance in public limited companies ensures regulatory compliance and protects shareholder interests. It minimizes risk of fraudulent activities and enhances operational efficiency. Companies with solid governance frameworks tend to achieve long-term success through better risk management. Effective governance also boosts company reputation and strengthens investor confidence. Well-governed firms attract more investors, leading to higher market capitalization. Research indicates that strong governance improves access to capital and reduces the cost of equity.
Building and maintaining investor trust
Investor relations are crucial for maintaining shareholder trust, starting with transparency in financial and operational disclosures. Regular reports and updates ensure investors have the information needed for informed decisions. Adhering to global reporting standards, such as IFRS or GAAP, reinforces credibility. Beyond transparency, effective communication is essential in strengthening investor confidence. Proactive engagement through meetings, press releases, and earnings calls fosters openness.
Roles and responsibilities of corporate boards
The corporate board plays a central role in shaping a company’s governance framework and ensuring its strategic objectives align with shareholder interests. Board members oversee executive management, enforce internal controls, and ensure regulatory compliance. A well-structured board includes professionals with diverse expertise, enhancing decision-making and risk management.
Emphasizing independence and accountability helps mitigate conflicts of interest, with many jurisdictions requiring non-executive directors. The rise of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria has further expanded board responsibilities, integrating sustainability into corporate strategies. Strong governance fosters investor trust, reinforcing long-term business stability. This interdependence between governance and investor relations creates a cycle of growth and market confidence.
Preparing a company for stock exchange listing
The company's preparation for stock exchange listing is vital for ensuring a smooth transition and setting the stage for a successful listing.
Assessing readiness for public listing
The first step in preparing a company for a stock exchange listing is evaluating its readiness. This assessment involves a comprehensive analysis of the company's financial health, market position, and compliance with applicable regulations.
- Financial stability: Companies must demonstrate consistent revenue streams, profitability, and robust cash flows. Evaluating the balance sheet for sufficient assets and minimal liabilities is also essential.
- Corporate structure: Companies should have a clear organizational structure, with well-defined roles and responsibilities. This setup facilitates smoother operations and compliance with governance standards.
- Market positioning: Understanding the competitive landscape and the company's unique value proposition is vital. It ensures that the company's story is compelling to potential investors and that it stands out in the market.
Necessary financial and legal preparations
A significant part of preparing for a listing involves financial and legal preparations, which are critical to ensuring compliance and building investor confidence.
- Financial audit and transparency: Conduct thorough financial audits with credible financial auditors to ensure accuracy and transparency in financial reporting. Companies often engage the services of reputable audit firms to bolster confidence among potential investors.
- Legal compliance: Engage with legal advisors to ensure that all legal aspects, including regulatory requirements, are addressed. This involves completing the necessary documentation, such as the Articles of Association, prospectus, and other legal disclosures.
- Corporate governance: Establishing strong corporate governance structures is paramount. This includes appointing a competent board of directors, setting up committees focusing on audit, risk, and remuneration, and implementing clear policies for managing conflicts of interest.
Selecting the right stock exchange for listing
Choosing the appropriate stock exchange is a strategic decision that can significantly affect a company’s public offering success. Various factors influence this decision:
- Market size and liquidity: Larger exchanges typically offer greater liquidity and visibility. For instance, listing on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the London Stock Exchange (LSE) can provide access to a broad investor base.
- Regulatory environment: Companies should consider the regulatory burdens associated with each exchange. Some exchanges have stringent reporting and compliance requirements, impacting operational agility.
- Costs and fees: The cost of listing, including initial fees, ongoing compliance costs, and other related expenses, should be weighed. Companies must ensure these align with their financial capacity and strategic objectives.
In preparing for a stock exchange listing, companies must take a holistic approach, considering financial health, legal compliance, corporate governance, and strategic market positioning. These preparations are foundational for attracting investors, maintaining transparency, and achieving a successful public debut. Each step in the preparation process builds toward a company’s readiness to meet the demands of being publicly traded, ultimately paving the way for growth and expansion in the public markets.
The United States stands as a prime destination for foreign investors, with a thriving business landscape and policies that foster innovation and global expansion. If you are ready to take your business to new heights, G2B’s Delaware offshore company formation service offers a seamless and strategic solution. As a trusted leader in professional business services, we specialise in helping entrepreneurs successfully establish and grow their ventures in the US.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
