In today's fast-paced business landscape, the pressure on corporate executives and outsourcing managers to streamline operations and cut costs is more intense than ever. Business process outsourcing (BPO) emerges as a strategic operational model that not only meets these needs but significantly enhances business scalability and efficiency. This article offers an exploration of BPO's strategic advantages, ranging from IT and customer support to offshore outsourcing.
This article is provided for general informational purposes to help new business owners and decision-makers better understand the fundamentals of BPO. We are specialists in the field of company formation, not providing consulting or advisory services related to operational management or outsourcing contracts. Therefore, this information should not be considered professional business advice. For tailored recommendations, please consult with a qualified BPO consultant or business strategy advisor.
What is business process outsourcing?
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) is a business strategy in which an organization contracts specific business operations or processes to an external third-party service provider. The goal is to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and leverage specialized expertise that may not be available in-house.
Key features of BPO
- Scope: BPO spans across industries such as healthcare, e-commerce, energy, pharmaceuticals, and more. It includes both back-office functions (e.g., accounting, IT services, human resources) and front-office tasks (e.g., customer support, marketing, sales).
- Technology integration: Modern BPO incorporates advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), robotic process automation (RPA), and cloud computing to enhance efficiency and scalability.
- Global reach: BPO can involve offshore outsourcing (vendors in different countries) or onshore outsourcing (domestic vendors). Offshore outsourcing is common for cost savings and access to global talent.
Need a free consultation with Delaware incorporation service? Let G2B help you navigate the process with confidence!
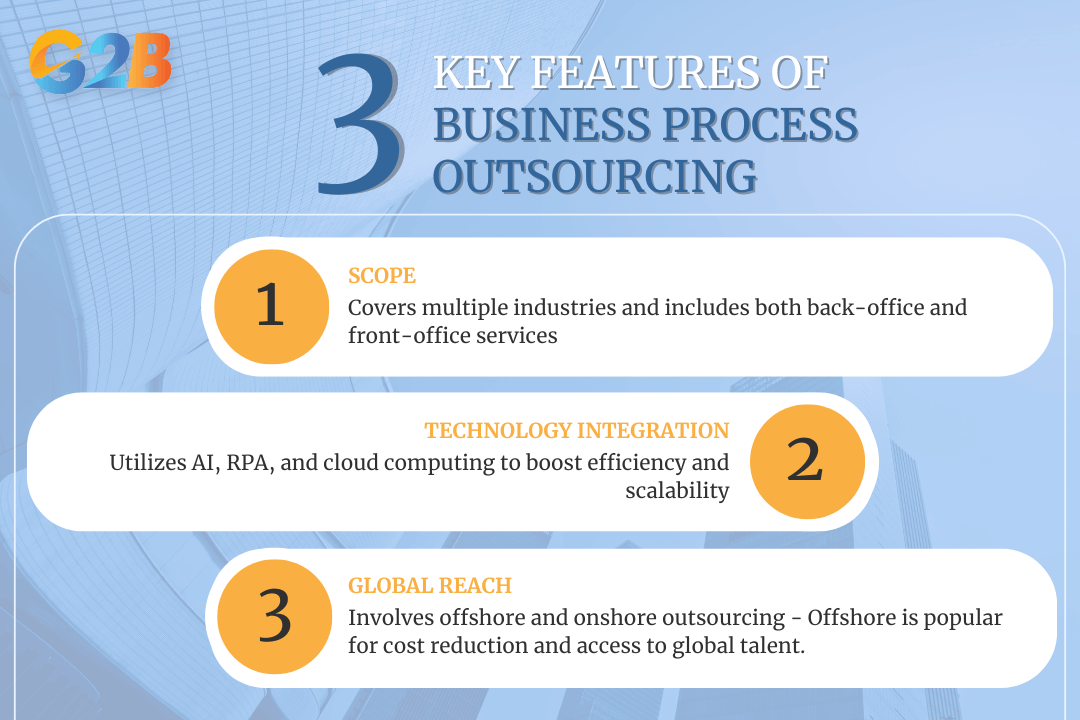
There are three key features of business process outsourcing
Roles of BPO in the modern business landscape
Business process outsourcing plays a pivotal role in today's business environment by offering companies the flexibility and agility needed to compete in a dynamic market. In essence, BPO allows businesses to:
- Focus on core competencies: By outsourcing non-essential tasks, organizations can concentrate resources and attention on strategic initiatives and core operations, fostering innovation and growth.
- Achieve cost efficiency: One of the most compelling reasons companies choose BPO is cost savings. Outsourcing can reduce operational costs significantly by leveraging economies of scale provided by specialized service providers.
- Access specialized expertise: BPO grants businesses entry to skills and technologies that may not be available in-house. This is particularly crucial in areas such as IT services where state-of-the-art technology and specialization are needed.
- Scalability and flexibility: Outsourcing providers offer scalability options that help businesses respond quickly to changing demands without the burden of managing extra resources in-house. This is vital for handling peak periods effectively and adapting to market changes promptly.
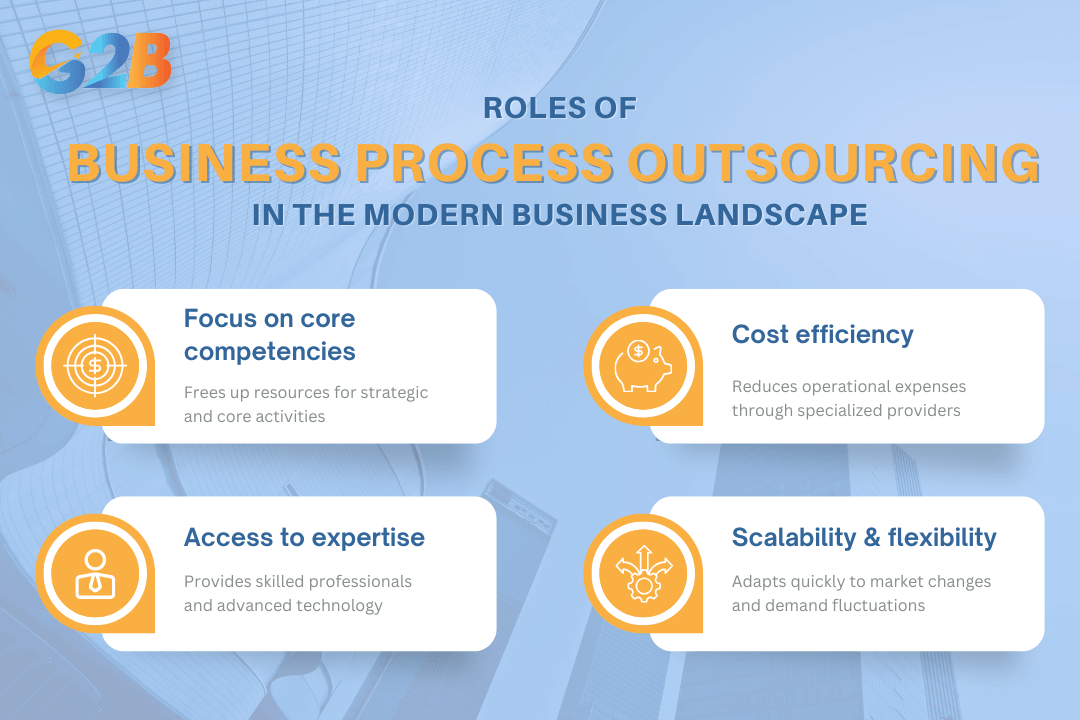
Investigating four roles of BPO in the modern business landscape
Key components of a successful BPO initiative
A successful BPO initiative hinges on several key components that need meticulous planning and execution:
- Strategic alignment: The BPO process must align with the company's overarching business strategy and objectives. Clear communication and understanding of how the outsourced process contributes to larger goals are essential.
- Vendor selection: Selecting the right service provider is crucial. Factors such as vendor expertise, financial stability, and cultural fit play a significant role in the decision-making process. Companies often evaluate these aspects by considering the vendor's track record and performance history.
- Data security and compliance: Maintaining robust data security measures is vital to managing the risks associated with BPO. Companies must ensure that the vendor complies with legal and regulatory requirements pertinent to data protection.
- Service level agreements (SLAs): Well-defined SLAs are imperative to set the expectations and performance standards for both parties. This includes metrics for quality, timelines, and deliverables, which govern the outsourcing relationship.
- Continuous monitoring and feedback: Regular performance evaluations and feedback loops ensure that the BPO processes remain efficient and aligned with the business’s evolving needs. This helps identify areas for improvement and adapt strategies accordingly.
BPO in various industries
Various industries leverage BPO to maximize operational efficiencies, drive innovation, and improve customer experience. Key industries that heavily utilize BPO include:
- IT services: IT outsourcing remains a staple, allowing businesses to access cutting-edge technology and talent without the burden of maintaining a large in-house IT team.
- Customer support: Many companies outsource customer service functions to improve service quality and extend support hours beyond in-house capabilities.
- Financial services: BPO in finance often involves accounting, payroll, and other financially-intensive processes to ensure precision and compliance with financial regulations.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers outsource billing, claims processing, and medical transcription to improve patient care outcomes.
Benefits of business process outsourcing
Business process outsourcing (BPO) serves as a strategic advantage for organizations seeking efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By leveraging third-party service providers, businesses can achieve multiple benefits that extend beyond mere financial savings.
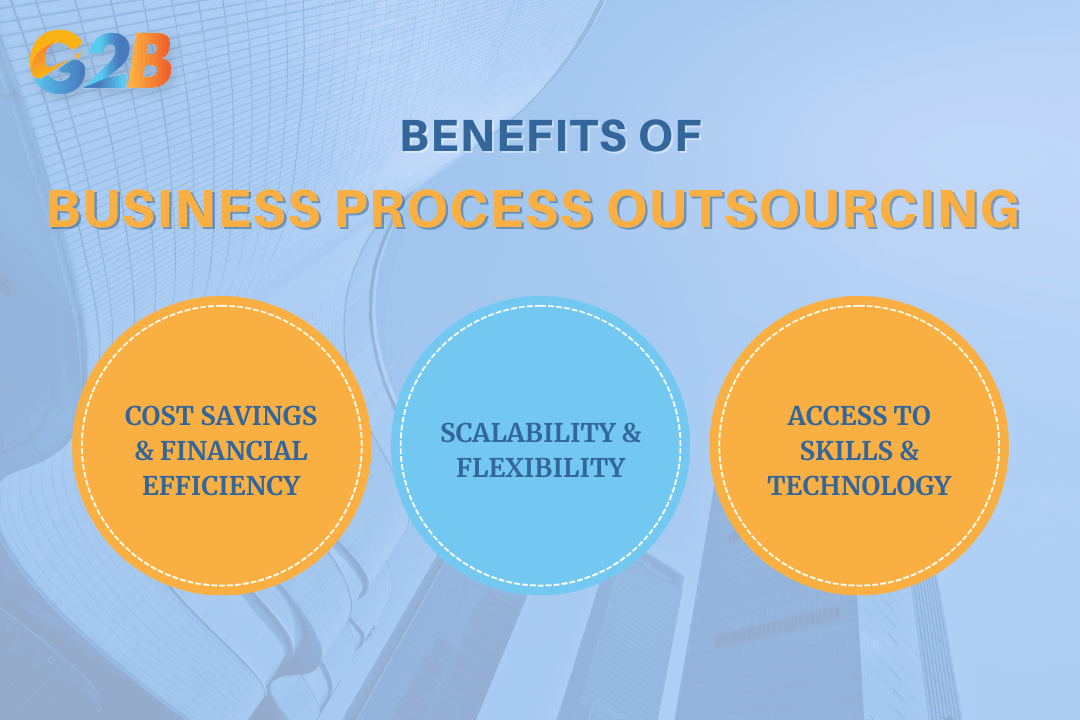
Business process outsourcing serves as a strategic advantage for organizations
Cost savings and financial efficiency
One of the primary drivers for adopting BPO is the potential for significant cost savings. These financial efficiencies enable businesses to reallocate resources towards core operations and strategic initiatives, offering a competitive edge in dynamic marketplaces:
- Labor cost reduction: Outsourcing allows firms to tap into global talent pools where labor is often more affordable. Countries like India, the Philippines, and Vietnam consistently rank as top BPO destinations due to their skilled yet cost-effective workforce.
- Operational and infrastructure savings: By outsourcing, companies eliminate the need to invest in expensive infrastructure and technology for non-core functions. The service provider bears these costs, spreading them across multiple clients.
- Variable cost structure: BPO transforms fixed costs into variable ones, allowing businesses greater financial flexibility. Companies pay only for the services they use, which is particularly beneficial during periods of economic uncertainty or demand variability.
Scalability and flexibility in business operations
BPO offers unparalleled scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt swiftly to market changes and operational demands. This adaptability is critical in today's fast-paced business environment:
- Rapid scaling: Businesses can quickly scale operations up or down without the traditional constraints of hiring or layoffs. For instance, a retail company facing peak demand during the holiday season can leverage BPO for temporary customer support expansion.
- Focus on core competencies: By outsourcing non-core processes like payroll, customer support, or IT services, companies can direct their focus and resources to core business activities and innovation, enhancing overall productivity and competitiveness.
- Risk management: Flexibility in operations minimizes risks associated with market fluctuations, enabling companies to pivot strategies without significant disruptions. For example, during economic downturns, businesses can reduce outsourced activities to manage costs effectively.
Access to specialized skills and technology
Outsourcing opens doors to a wealth of specialized skills and cutting-edge technologies that may not be otherwise accessible internally:
- Expertise and best practices: BPO providers are often industry leaders, bringing expertise and best practices to the table. This access is crucial in fields like finance and IT, where specialized knowledge significantly impacts operational success.
- Advanced technology: Technology vendors and consulting firms within the BPO space offer state-of-the-art solutions such as automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics. This access empowers businesses to leverage technologies without substantial investment, driving efficiency and innovation.
- Continuous improvement: BPO providers frequently update and refine their technologies and processes, ensuring that businesses benefit from the latest advancements without the burden of staying current. This continuous improvement cycle supports a culture of innovation and process optimization.
Risks and challenges of BPO
As the business process outsourcing (BPO) industry continues to expand, organizations must navigate various risks and challenges that accompany these initiatives.
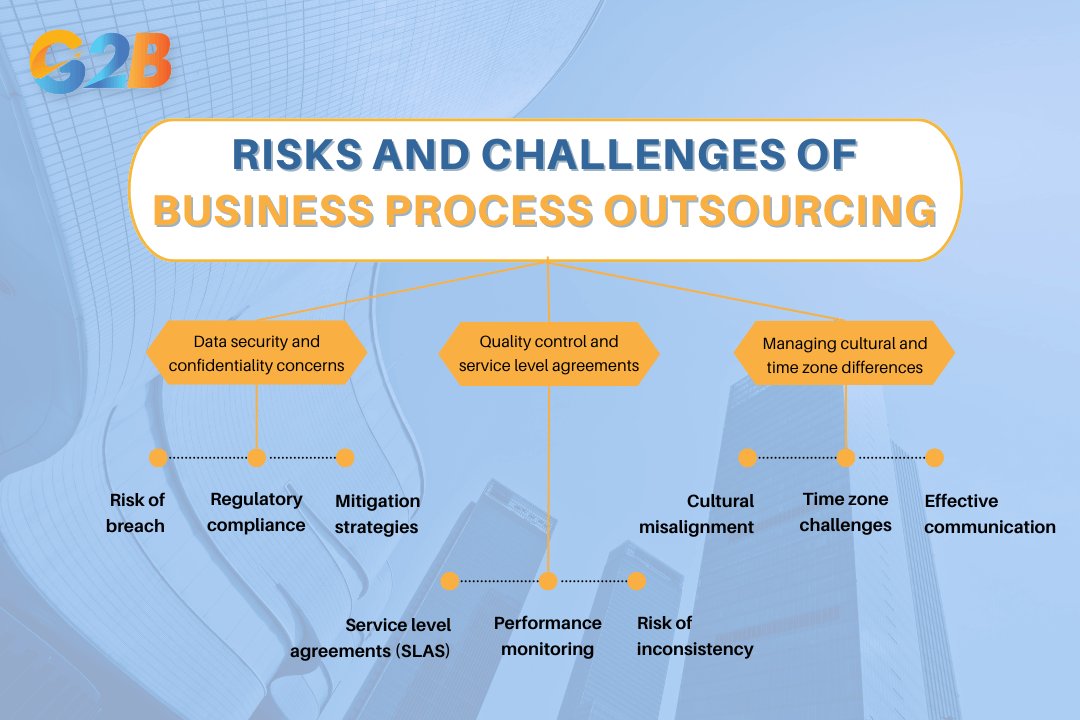
Organisations should navigate the risks and challenges of the BPO
Data security and confidentiality concerns
Data security remains one of the foremost challenges in BPO, as companies must entrust sensitive information to third-party providers:
- Risk of breach: When outsourcing, businesses expose themselves to potential data breaches from both external cyberattacks and internal threats, such as employee negligence or malicious behaviour within the outsourcing firm.
- Regulatory compliance: Companies also face challenges adhering to international data protection laws, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. Ensuring compliance requires both a comprehensive legal understanding and robust monitoring systems.
- Mitigation strategies: Companies can mitigate these risks by conducting thorough vendor assessments, implementing strict data processing agreements, and adopting advanced cybersecurity measures. Encryption, regular security audits, and employee training on data protection practices are essential to safeguarding information.
Quality control and service level agreements
Maintaining quality control is another significant challenge in BPO, where service delivery often occurs far from the client’s direct oversight.
- Service level agreements (SLAS): Establishing clear and enforceable SLAs is vital for managing expectations and ensuring consistent service quality. These agreements should detail specific performance metrics, penalties for non-compliance, and pathways for dispute resolution.
- Performance monitoring: Businesses should employ ongoing monitoring and performance evaluation, utilizing tools such as real-time dashboards and bi-annual reviews to maintain visibility over the outsourced operations.
- Risk of inconsistency: There is always a threat of the service provider’s performance deteriorating, adversely affecting the client’s reputation and operational efficiency. Aligning goals and nurturing a collaborative relationship can help address these challenges.
Managing cultural and time zone differences
Cultural and temporal variances pose additional obstacles in BPO, particularly in offshore outsourcing scenarios.
- Cultural misalignment: Divergent cultural norms can lead to misunderstandings or miscommunications, impacting team cohesion and project outcomes. Creating cross-cultural training programs and embracing diversity within teams can bridge these gaps.
- Time zone challenges: Time zone disparities complicate communication, coordination, and project management, often resulting in delays and reduced productivity. Utilizing overlapping hours for key meetings and adopting asynchronous communication tools can help mitigate these issues.
- Effective communication: Building robust communication protocols by relying on video conferencing, collaborative platforms, and regular updates can guide teams through these challenges. Human resource policies must incorporate flexibility and adaptability to different working hours and environments.
Setting up a company in Vietnam? Let G2B simplify the process - Book your free consultation now!
Types of BPO services and global trends
Business process outsourcing (BPO) has become an integral strategy for organizations aiming to optimize operational efficiency and focus on core competencies. This part will delve into the varied types of BPO services and explore the emerging global trends.
IT Outsourcing, Customer Support, and HR services
BPO services encompass a broad spectrum, primarily categorized into front-office and back-office solutions. In the realm of back-office operations, IT outsourcing remains pivotal, handling critical tasks such as software development, infrastructure management, and technical support. IT outsourcing allows companies to access advanced technology and specialized expertise without substantial capital investment.
Another essential category is customer support outsourcing, where businesses delegate functions like call center management, helpdesk services, and customer engagement to third-party providers. This service type leverages managed services to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty through efficient and scalable solutions.
Human Resources (HR) outsourcing is increasingly popular, covering activities such as recruitment, payroll processing, and employee training. By outsourcing HR functions, organizations can streamline their operations and focus on strategic HR initiatives, thus fostering talent development and organizational growth.
Emerging trends in the global BPO market
The BPO industry is witnessing a transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving business needs. One notable trend is the rise of robotic process automation (RPA), which automates repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing human error. This integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in BPO services offers enhanced data processing capabilities, driving business outcomes.
Another trend is the emphasis on cloud-based services, which provide scalable solutions and foster greater flexibility in service delivery. Cloud services enable BPO providers to offer customized solutions tailored to specific client requirements, fostering a more agile business environment.
Data security and privacy have gained prominence due to increasing concerns about data breaches and regulatory compliance. As a result, BPO providers are investing heavily in advanced security protocols and compliance frameworks to build trust and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of client data.
Offshore vs onshore outsourcing dynamics
The decision between offshore and onshore outsourcing is a critical consideration for businesses. Offshore outsourcing is the practice where a company hires a third-party service provider in a foreign country to handle certain business functions or processes instead of performing them in-house. It involves contracting services to providers in different countries, often in regions like India or the Philippines, known for cost-effective labor and skilled talent pools.
Conversely, onshore outsourcing, or domestic outsourcing, involves engaging service providers within the same country. This model offers advantages in terms of cultural alignment, time zone synchronization, and easier communication. While typically more costly than offshore solutions, onshore outsourcing is preferred for functions that require high levels of collaboration and regulatory compliance.
How to implement a BPO strategy
Implementing a BPO strategy is a multi-faceted process that requires careful planning and execution to ensure alignment with organizational goals. This strategic approach can bring about significant cost savings and operational efficiency.
Step-by-step guide to BPO implementation
- Conduct a needs assessment
- Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your organization's processes. Identify non-core functions that could benefit from outsourcing, such as accounting, HR, or IT services. These are tasks that, while necessary, do not drive the company's primary business goals directly.
- Define goals and objectives
- Establish clear, achievable goals for outsourcing. Are you looking to reduce costs, access specialized skills, or improve service delivery? Clear objectives will guide the selection of the appropriate functions to outsource and help in setting performance benchmarks.
- Identify suitable functions for outsourcing
- Carefully analyze and select functions that are non-core yet crucial. Functions like back office operations, customer support, or data entry often make strong candidates for outsourcing due to their process-driven nature.
- Select the right vendor
- Vendor selection is critical and should be based on expertise, reputation, and cultural fit. Evaluate potential partners using criteria like their track record, financial health, and ability to deliver on service-level agreements (SLAs).
- Develop a transition plan
- Create a comprehensive transition plan that includes timelines, milestones, and risk management strategies. This plan should address potential challenges such as data security, quality control, and the integration of vendor systems with internal processes.
Identifying non-core functions suitable for outsourcing
Identifying which functions to outsource involves a strategic analysis of the company's operational framework. Non-core functions typically possess the following characteristics:
- Process-driven: Tasks that rely on repetitive processes and established protocols are often best suited for outsourcing.
- Resource-intensive: Functions that require significant internal resources but do not contribute to core business objectives are prime candidates.
- Scalable needs: Operations that need scaling up or down rapidly due to market demands can benefit from the flexibility that BPO offers.
Setting clear objectives and measurable KPIs
Clear objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential to ensure the BPO strategy's success and to measure performance. Consider the following when establishing objectives and KPIs:
- Cost savings: Determine a percentage or specific amount you aim to save through outsourcing.
- Quality improvements: Set targets for quality enhancements, such as reduced error rates or faster processing times, to ensure that outsourcing not only saves money but also improves service quality.
- Efficiency gains: Use KPIs to track efficiency metrics, such as turnaround times for customer service inquiries or the time taken to complete back-end processes.
- Risk mitigation: Develop KPIs that focus on minimizing risks, for example, the percentage of compliance with data security standards.
FAQs about business process outsourcing
This part will address frequently asked questions to clarify crucial aspects of BPO and provide valuable insights for organizations contemplating outsourcing strategies.
What factors should companies consider before outsourcing?
Before initiating a BPO strategy, companies must evaluate various factors to ensure alignment with their business goals:
- Core vs. non-core activities: Identify which processes are non-core yet crucial for operational efficiency. Outsourcing non-core tasks like back-office processing allows companies to focus on their primary business functions.
- Vendor expertise and fit: Assess potential outsourcing partners for their expertise in specific industries and how well their culture aligns with your company's. Solid communication and cultural compatibility are vital for a successful partnership.
- Cost analysis: Conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, considering not just immediate financial savings but also long-term implications like potential hidden costs or transition expenses associated with BPO.
- Data security and compliance: Ensure rigorous data protection practices are in place. Companies should prioritize vendors who comply with international data protection standards to mitigate the risk of data breaches.
- Technology and infrastructure: Consider the technology and infrastructure capabilities of potential vendors. A provider with robust IT infrastructure can facilitate seamless integration and support technological upgrades.
How can BPO impact business growth and transformation?
Business process outsourcing, when strategically implemented, can significantly drive growth and transformation:
- Scalability: BPO offers scalability, allowing businesses to quickly adjust the scale of operations to match demand fluctuations without the burden of additional permanent resources.
- Access to advanced skills and technology: Outsourcing grants access to a talent pool with specialized skills and cutting-edge technologies that might be costly or strategic for a company to develop internally.
- Focus on core competencies: By delegating non-core functions, companies can dedicate more resources and attention to innovate and improve their core competencies, fostering business growth.
- Efficiency and speed: Outsourcing can streamline business processes, improve efficiency, and reduce cycle times as external vendors often implement best-in-class practices.
What are common misconceptions about BPO?
While BPO has evolved as a strategic business tool, several misconceptions still exist:
- Only cost-saving focus: While cost reduction is a significant advantage, it is not the sole benefit. BPO also enhances operational efficiency, quality, and speed, contributing to overall business agility.
- Quality compromise: Many believe outsourcing leads to quality degradation. However, reputable BPO providers focus on maintaining high service quality and meeting service level agreements (SLAs).
- Loss of control: Fear of losing control over outsourced processes is prevalent. In reality, effective relationship management and regular performance reviews can ensure a balanced and productive partnership.
- Applicable only for large enterprises: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can equally benefit from BPO. It provides SMEs with competitive advantages by leveraging resources and expertise they may lack internally.
In conclusion, business process outsourcing, when approached strategically, can be a powerful tool for business growth and efficiency. By staying informed about industry innovations and maintaining a clear focus on strategic objectives, companies can harness the full advantages of BPO, positioning themselves for sustained success in a competitive global market.

 Delaware (USA)
Delaware (USA)  Vietnam
Vietnam  Singapore
Singapore  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  United Kingdom
United Kingdom 
